Design
See also: |
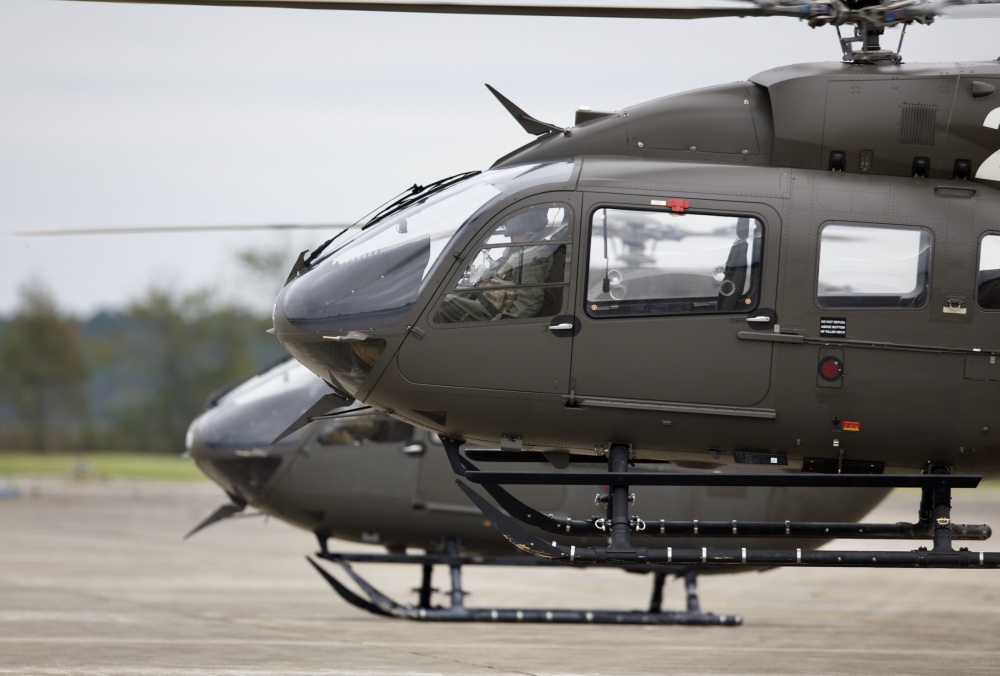
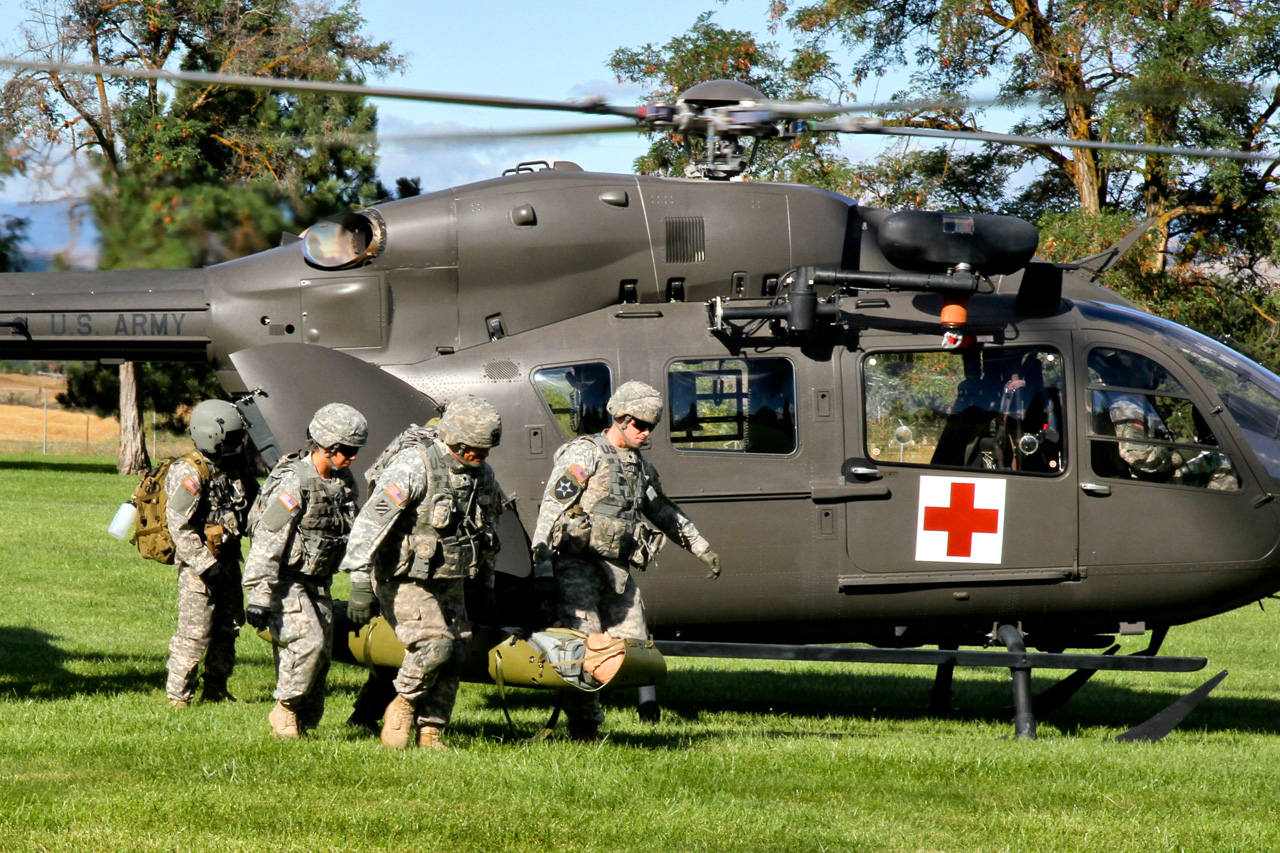
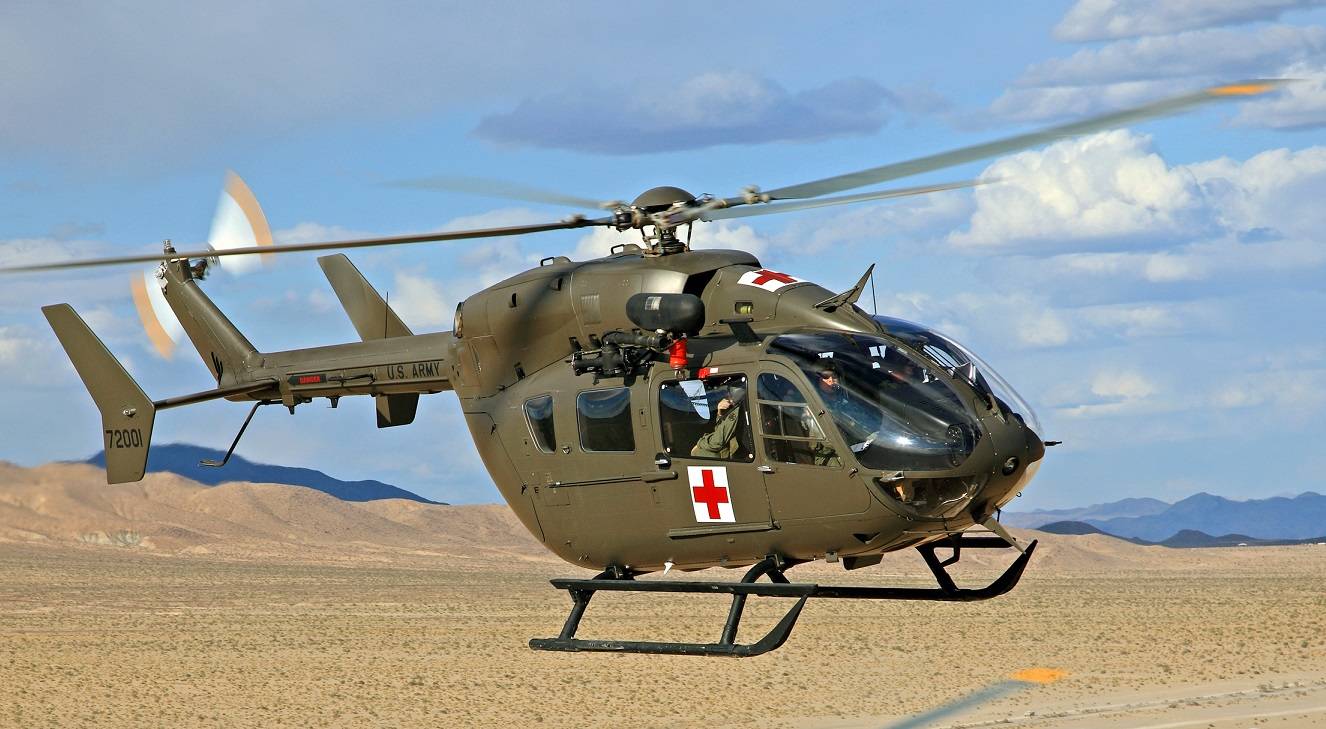
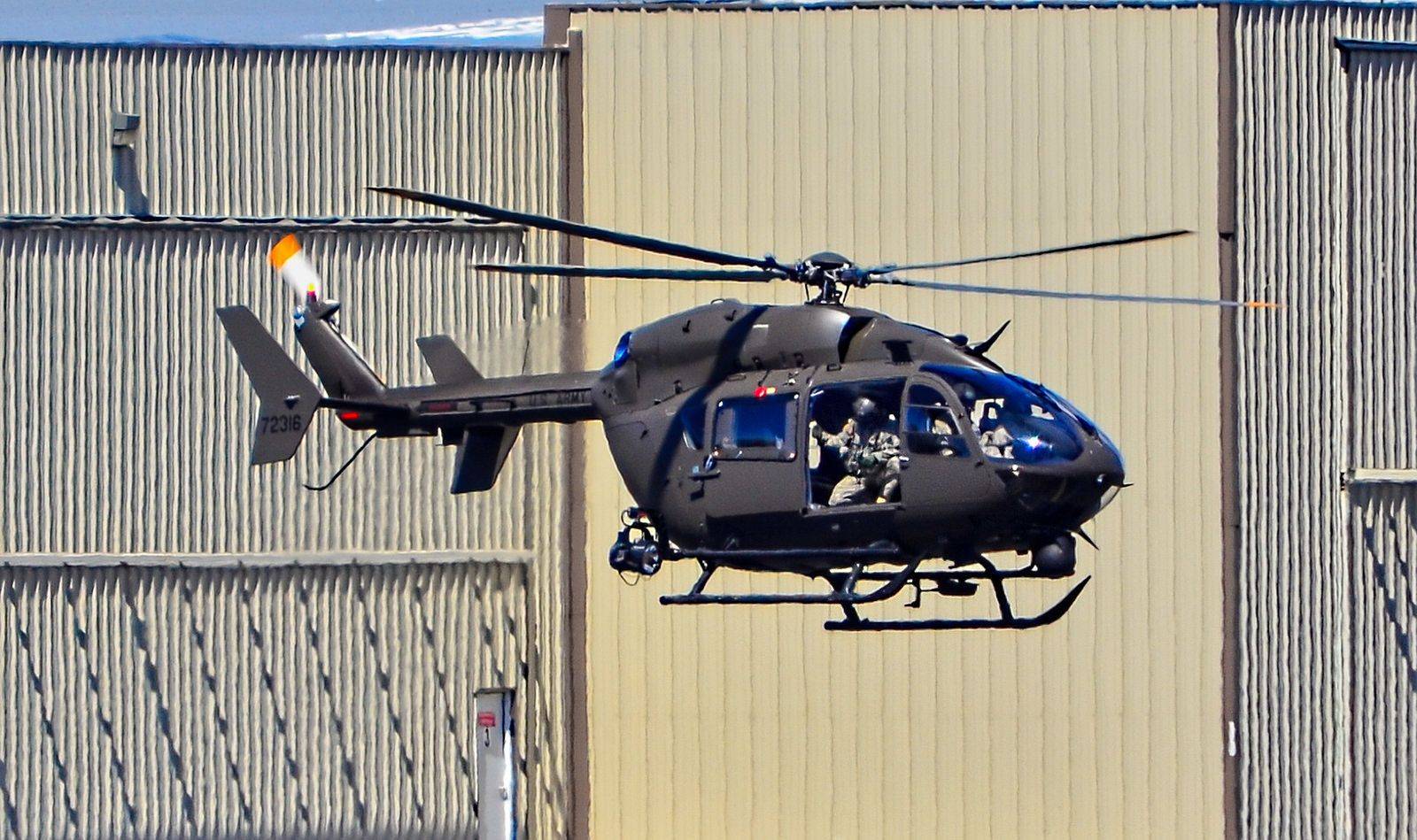
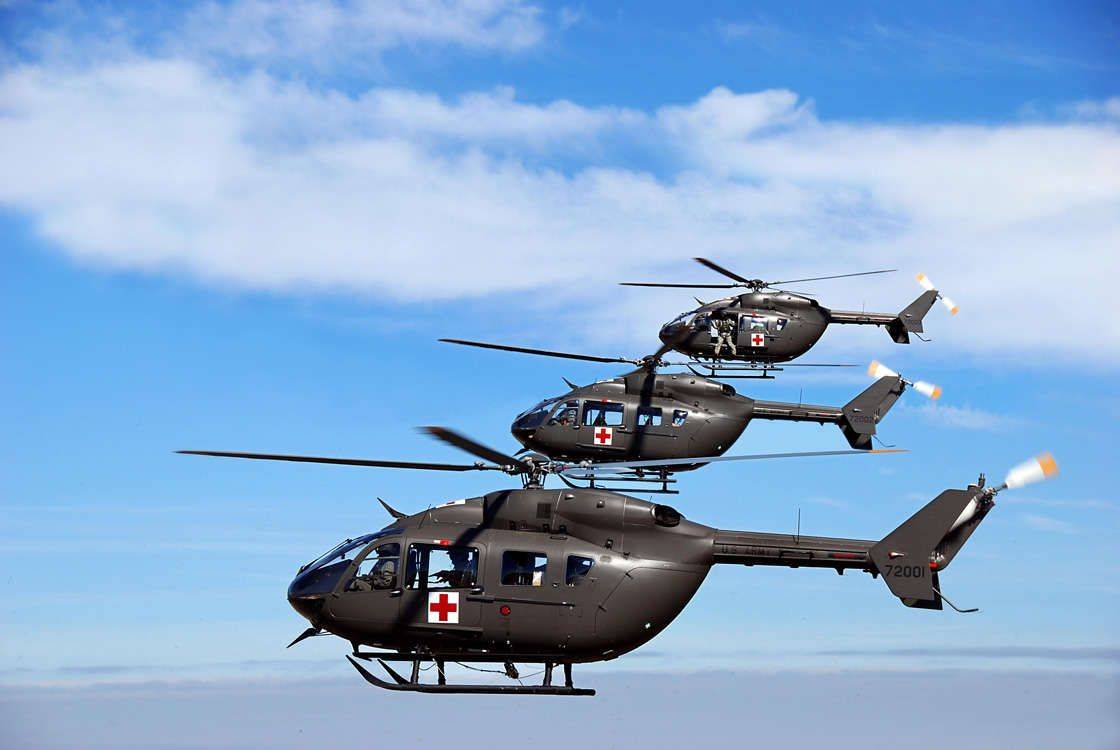
UH-72A with MEDEVAC package
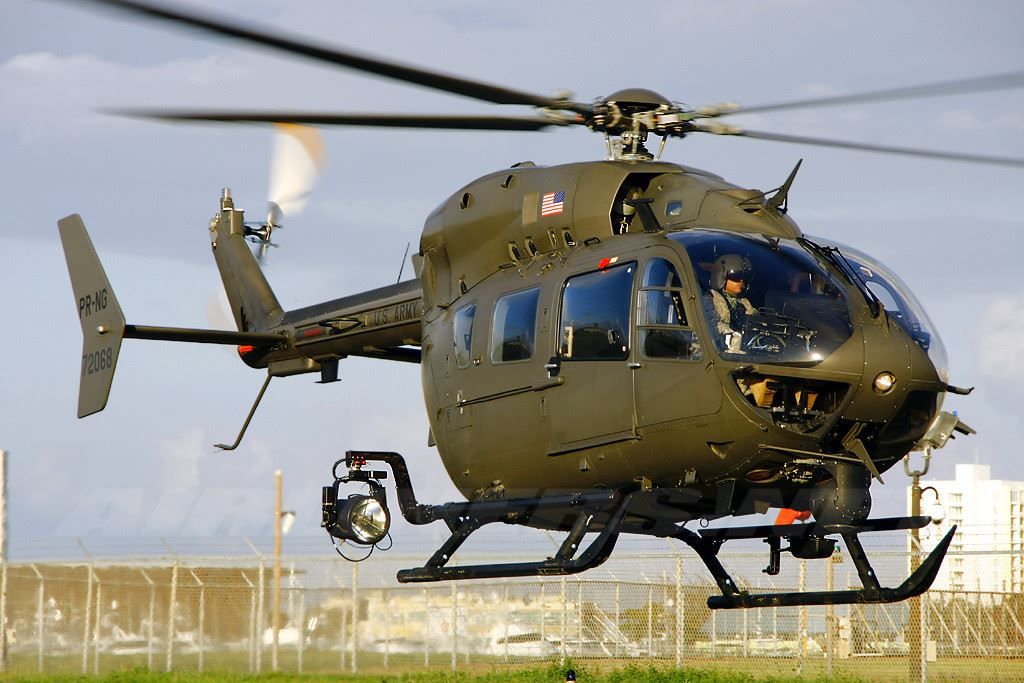
The UH-72 is designed to take on a range of missions, from general support and medical evacuation (MEDEVAC) to personnel recovery and counter-narcotics operations. They are planned to replace the UH-1 and OH-58A/C, which are older light utility helicopters, and supplant other types in domestic use, primarily those in Army National Guard service. The UH-72 is being procured as a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) product, which simplifies logistics support of the fleet. EADS NA has teamed with Sikorsky to provide Contractor Logistics Support (CLS) for the UH-72, through its Helicopter Support, Inc. (HSI)/Sikorsky Aerospace Maintenance. (SAM) subsidiaries.
Proposed uses
The Armed Scout 645 (EC645) was a proposed armed version of the UH-72 for the US Army’s Armed Aerial Scout (AAS) program for an OH-58D replacement. On 4 May 2009, EADS and Lockheed Martin announced a teaming agreement for the 645. Three demonstrator AAS-72X aircraft were built and began flight testing in late 2010. In September 2012, EADS began voluntary flight demonstrations of both an AAS-72X and an EC145 T2 at high altitudes, reportedly meeting with performance requirements. Two versions were offered: the AAS-72X, an armed version of the UH-72; and the AAS-72X+, an armed militarized version of the EC-145T2. In late 2013, the US Army announced the termination of the AAS program.
In May 2012, the UH-72A was submitted in the US Air Force’s Common Vertical Life Support Platform (CVLSP) program for a UH-1N Twin Huey replacement. As with the US Army, the UH-72A can operate in permissive environments, such as ICBM site support and security under the Air Force Global Strike Command and personnel transport in the National Capital Region by the Air Mobility Command’s 89th Airlift Wing. Advantages over the UH-1N include 30 percent more speed, range, and loiter time, enhanced reliability and crashworthiness, night vision compatibility, modern avionics, and being cheaper to operate. In August 2013, the USAF said it planned to sustain the UH-1N for six to ten more years. In September 2013, acting Air Force Secretary Eric Fanning received a letter from the CEO of EADS North America, arguing that to refit and maintain the Hueys costs more than to acquire and operate UH-72As; the letter also urged prompt action as Army orders were almost complete and production was winding down. The USAF said it had insufficient funding for such a procurement and can risk using Hueys for a while. EADS North America stated that the UH-72A “will lower the risk to the U.S. Air Force nuclear enterprise, and will save taxpayers the considerable cost of future recapitalization.” Reportedly, buying UH-72As would cost as much as upgrading 62 Hueys, but long-term operating costs would be much lower.
Bell UH-1 Huey [1956]
В значительной степени синонимичный технологии войны во Вьетнаме, UH-1 был простым и практичным вертолетом, который приобрел легендарный статус благодаря своим подвигам. Это было прочное, недорогое и как раз то, что нужно армии США для доставки тысяч солдат посреди густых северовьетнамских джунглей. Приводимый в действие одним двигателем, UH-1 мог перевозить в бой 10-14 военнослужащих. Основным вооружением был пулемет М60, установленный на каждой двери, которым управлял стрелок. Чтобы защитить пилотов от наземного огня, сиденья были бронированы, а экипажу были выданы бронежилеты для дополнительной защиты во время опасных полетов.
Другой важной ролью “Хьюи” была эвакуация раненых, когда ему удавалось транспортировать раненых солдат с поля боя в боевые госпитальные подразделения за час или два. Это значительно помогло сократить потери американцев во время войны, поскольку раненые могли получить немедленную медицинскую помощь.Было построено более 16 000 таких универсальных машин, и они до сих пор используются Корпусом морской пехоты США в форме UH-1Y
Development
LUH Program and UH-145
LUHMD ExplorerAW139EADS North AmericaUH-145EC 145UH-72ALakotaColumbus, MississippiEurocopter DeutschlandArmy Chief of StaffRay OdiernoUS Army National GuardUH-60 Black HawkUnder Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology and LogisticsFrank Kendall
Trainer use
US Army ReserveTH-67 CreekUnited States Army Aviation Center of ExcellenceFort Rucker, AlabamaAgustaWestlandBell Helicopterauto-rotationsGerman Army
Proposed uses
Armed Aerial ScoutLockheed MartinAAS-72XEC-145T2UH-1N Twin HueyICBMAir Force Global Strike CommandNational Capital Region89th Airlift Wingcrashworthinessnight vision compatibilityEric Fanning
Дизайн [ править ]
UH-72A Lakota с пакетом MEDEVAC
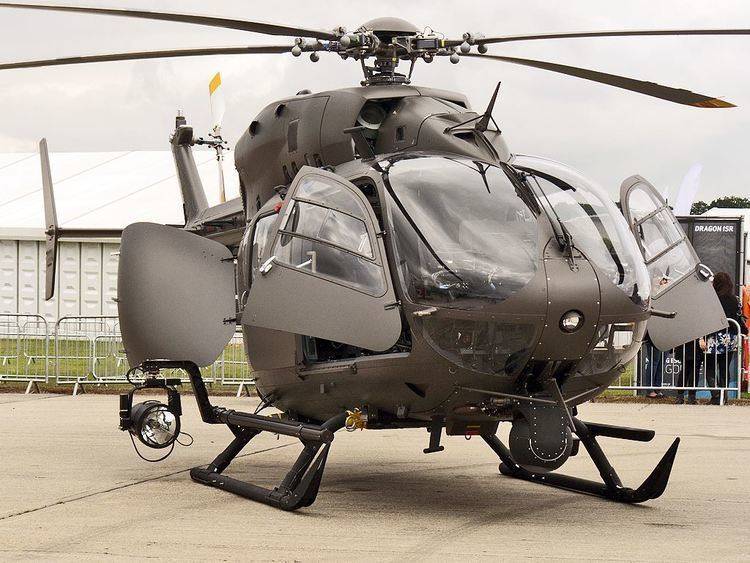
UH-72 предназначен для выполнения ряда задач, от общей поддержки и медицинской эвакуации ( MEDEVAC ) до восстановления персонала и операций по борьбе с наркотиками. Планируется, что они заменят старые легкие универсальные вертолеты UH-1 и OH-58A / C и вытеснят другие типы, используемые в быту, в первую очередь те, которые используются в Национальной гвардии . UH-72 закупается как готовый коммерческий продукт (COTS), что упрощает логистическую поддержку флота. EADS NA объединилась с Sikorsky для обеспечения логистической поддержки подрядчиков (CLS) для UH-72 через свою компанию Helicopter Support, Inc. (HSI) / Sikorsky Aerospace Maintenance. (SAM) дочерние компании.
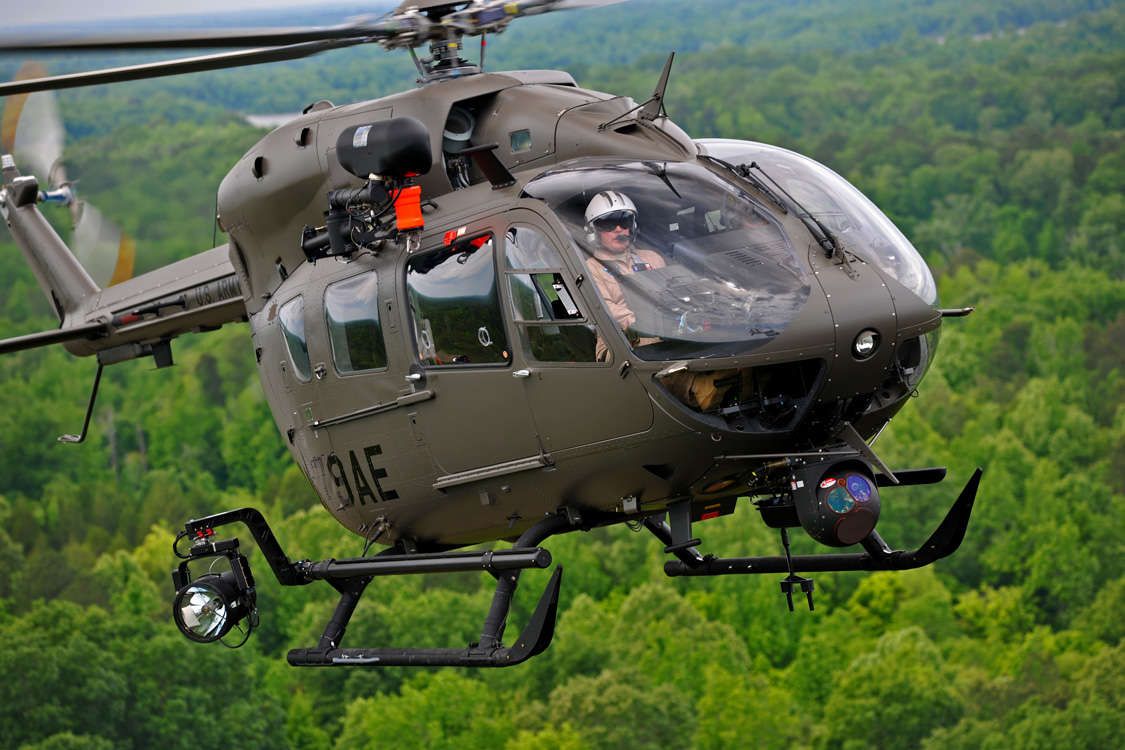
Базовый UH-72A – это просто коммерческий вертолет EC145, имеющий цветовую схему армии США и оборудованный радиостанцией AN / ARC-231 . Помимо служебного транспорта, Lakota может быть настроен для медицинской эвакуации, VIP-транспорта, обеспечения безопасности и поддержки, а также для обучения противостоящих сил. Он описывается как лучший военный самолет на вооружении для внутренних операций, используемый Национальной гвардией армии для государственной поддержки, оказания помощи при бедствиях и защиты территории страны, а также неразвернутыми активными частями для медицинской эвакуации и обучения. По сравнению с предыдущим UH-1 HueyИспользуемый в этих ролях двухмоторный Lakota летает быстрее (145 узлов, или 269 км / ч, или 167 миль в час против 124 узлов, или 230 км / час, или 143 миль в час), имеет внешнюю подъемную систему и полностью интегрированную компьютеризированную кабину. Huey имеет преимущество в роли MEDEVAC, поскольку он может перевозить трех пациентов по сравнению с грузом Lakota для двух пациентов, но в среднем эвакуация обычно проводится с двумя или меньшим числом пациентов. Комплект оборудования для обеспечения безопасности и поддержки (S&S MEP), установленный на UH-72A, позволяет выполнять миссии по обеспечению внутренней безопасности, борьбе с наркотиками и пограничному патрулированию. Этот пакет включает в себя электрооптический / инфракрасный датчик и турель с лазерным указателем, систему движущихся карт и сенсорные дисплеи, систему управления видео, цифровую видеозапись и канал передачи данных, прожектор и спасательный подъемник из пакета MEDEVAC.
Design
The UH-72 is designed to take on a range of missions, from general support and medical evacuation (MEDEVAC) to personnel recovery and counter-narcotics operations. They are planned to replace the UH-1 and OH-58A/C, which are older light utility helicopters, and supplant other types in domestic use, primarily those in Army National Guard service. The UH-72 is being procured as a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) product, which simplifies logistics support of the fleet. EADS NA has teamed with Sikorsky to provide Contractor Logistics Support (CLS) for the UH-72, through its Helicopter Support, Inc. (HSI)/Sikorsky Aerospace Maintenance. (SAM) subsidiaries.
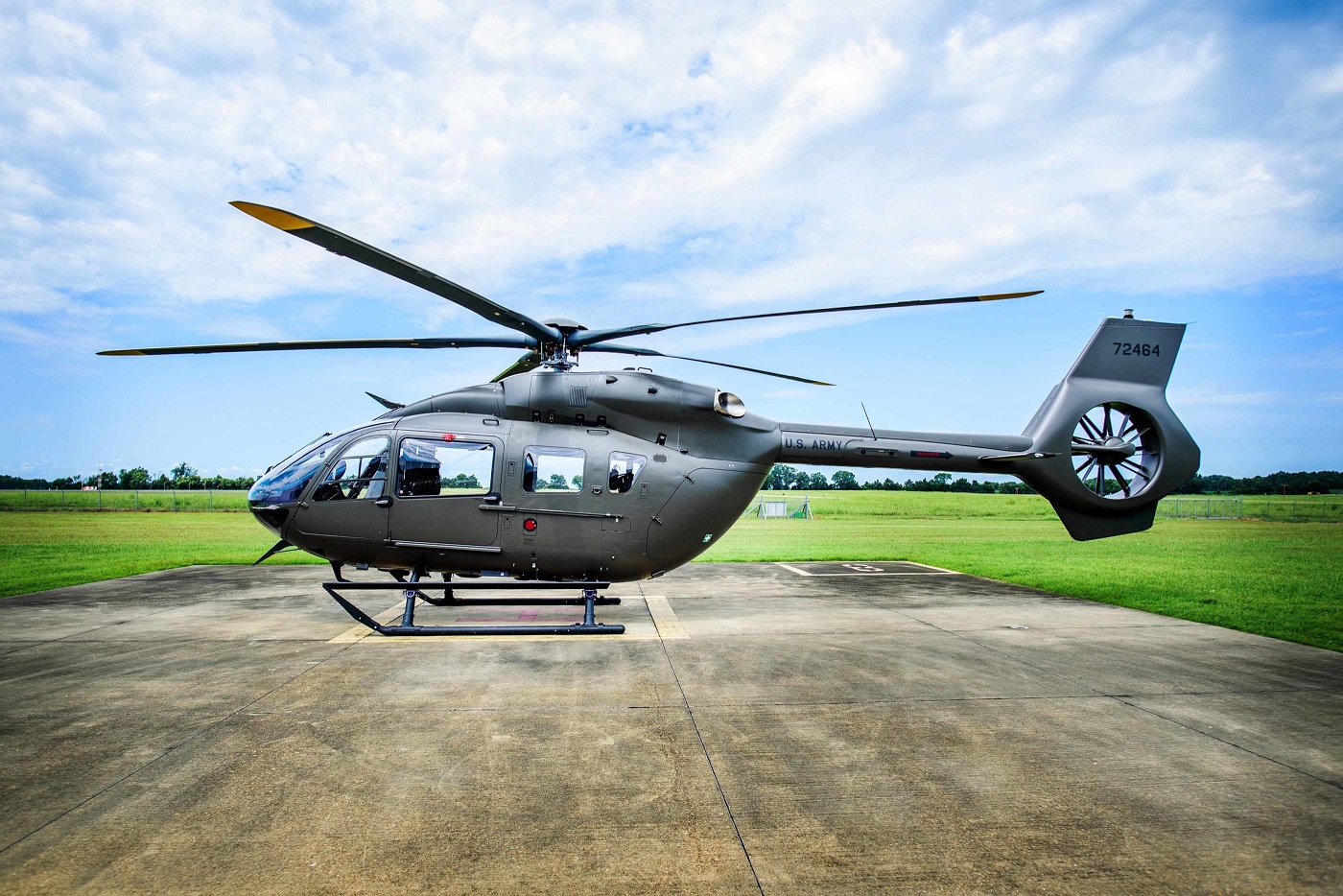
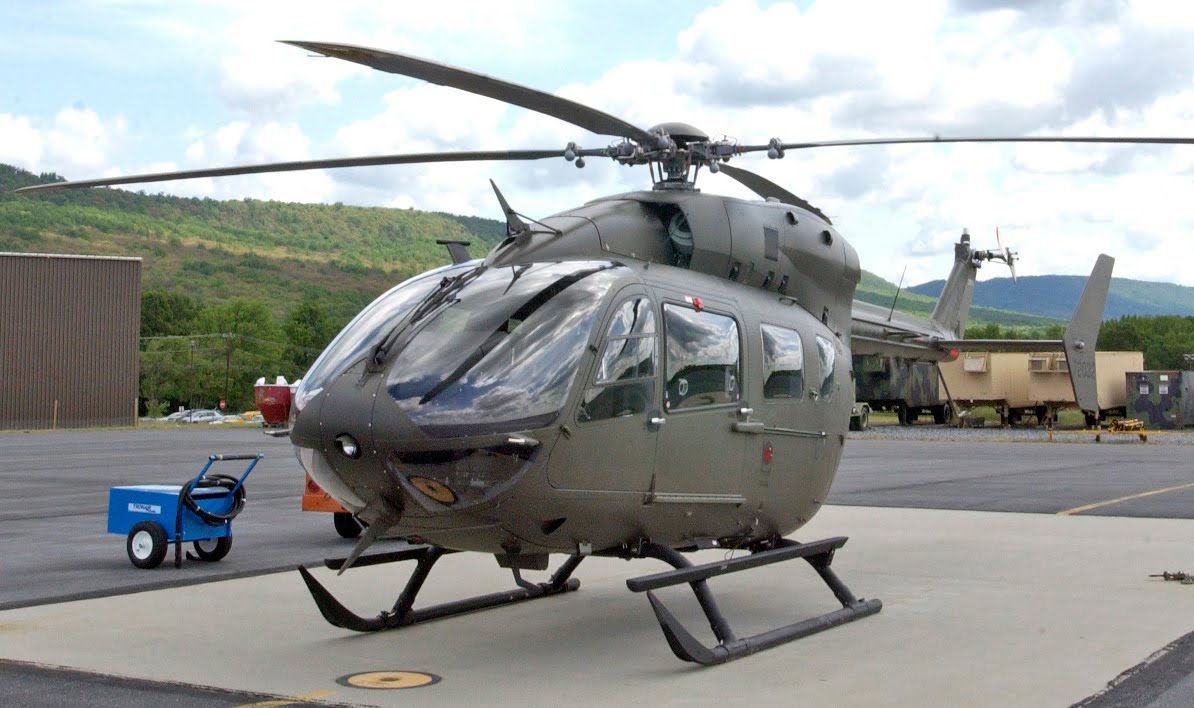
The basic UH-72A is simply a commercial EC145 helicopter that has a US Army color scheme and is fitted with an AN/ARC-231 radio. Other than utility transport, the Lakota can be configured for medical evacuation, VIP transport, security and support, and opposing forces training. It is described as the best military aircraft in the inventory for domestic operations, used by the Army National Guard for state support, disaster relief, and homeland defense and by non-deployed active units for MEDEVAC and training. Compared to the previous UH-1 Huey used in those roles, the twin-engine Lakota flies faster (145 kn or 269 km/h or 167 mph versus 124 kn or 230 km/h or 143 mph), has an external hoist system, and has a fully integrated computerized cockpit. The Huey has an advantage in the MEDEVAC role, being able to carry three patients compared to the Lakota’s two-patient load, but an average evacuation typically deals with two or fewer patients. The Security & Support Mission Equipment Package (S&S MEP) is a version of the UH-72A for homeland security, counter drug, and border patrol missions. It is equipped with an electro-optical/infrared sensor and laser pointer turret, moving map system and touch-screen displays, video management system, digital video recorded and datalink, searchlight, and rescue hoist from the MEDEVAC package.
Turbomeca Arriel 1E2 turboshaft engines and flight training
The helicopter is powered by two Turbomeca Arriel 1E2 turboshaft engines, each providing 550kW of take-off power and 516kW continuous power.
The engines are rated to provide a maximum power of 574kW for two and a half minutes and 404kW continuously in one-engine-inoperable-mode fight.
CAE USA in Tampa, Florida, was contracted to design and manufacture UH-72A cockpit procedural trainers for the US Army, used for procedural, familiarisation, and transition training as the army begins taking delivery of the UH-72A helicopters.
Airbus Group also acquired the UH-72A cockpit procedural trainer to support pilot transition training at the Airbus Helicopters training centre in Grand Prairie, Texas.
Operational history
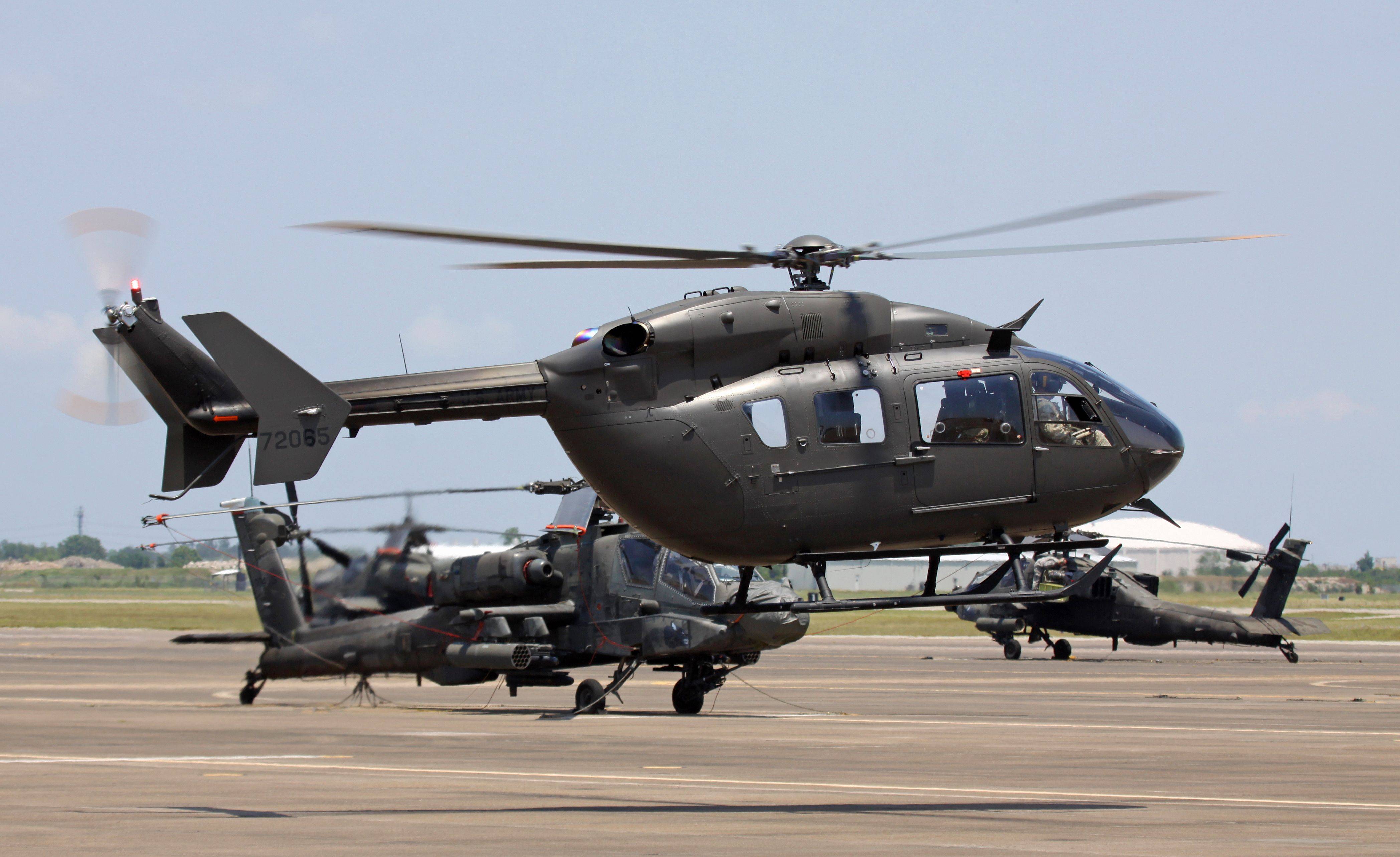
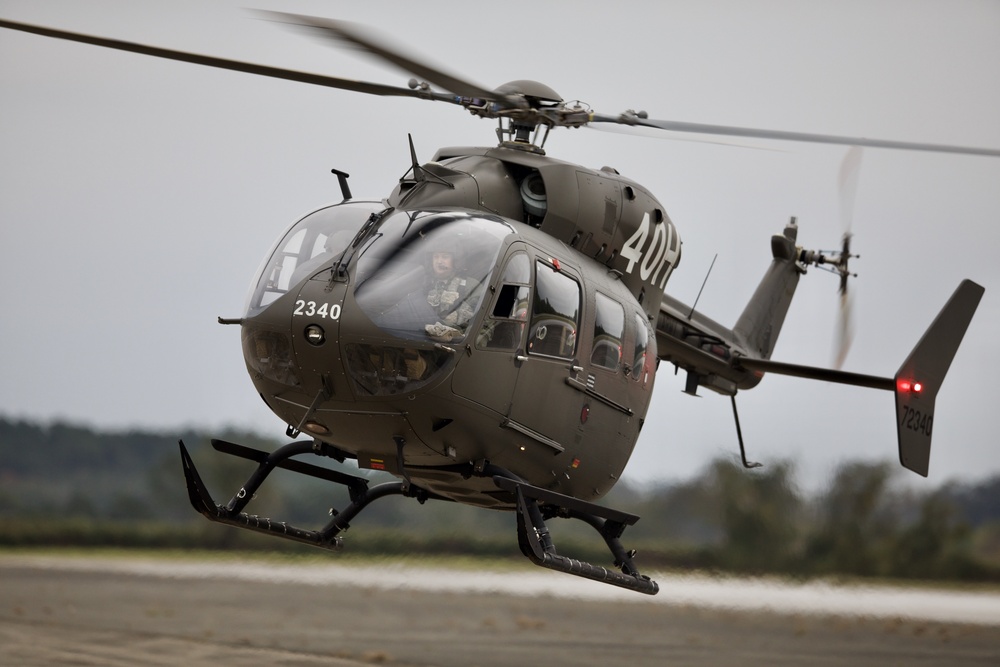
File:First Two Army National Guard UH-72A Lakotas 9 June 2008, Mississippi.jpg
The first two Army National Guard UH-72As at Tupelo, Mississippi
The first aircraft was delivered to the US Army on 11 December 2006 in Columbus, Mississippi. On 12 December 2006, General Richard A. Cody, Vice Chief of Staff of the Army, and Joe Red Cloud, a chief of the Oglala Sioux Tribe, Lakota nation, accepted the first UH-72A in an official ceremony. The service estimated that delivery of the planned 345 aircraft would continue until 2017.
The first production helicopters were sent to the National Training Center (NTC), Fort Irwin, California for medical evacuation missions in January 2007. On 20 June 2007, the NTC’s US Army Air Ambulance Detachment (USAAAD) became the first operational unit to field the Lakota. On 10 July 2007, the Training and Doctrine Command (TRADOC) Flight Detachment at Fort Eustis, Virginia became the second US Army unit fielded with the UH-72A.
A report published in August 2007 by the Operational Test and Evaluation Directorate (DOT&E) noted that although the Lakota “…is effective in the performance of light utility missions,” it was prone to overheating during operations in the desert conditions of Fort Irwin when not equipped with air conditioning systems. In response, vents were added in the doors to increase cabin air flow; air conditioning has been installed on some Medical and VIP versions, as well as added air conditioning units for crew comfort.
The (JRTC) located at Fort Polk, Louisiana received their first aircraft on 7 September 2007. On 16 January 2009, the United States Military Academy received two UH-72As, replacing two UH-1H helicopters for VIP transport to and from the academy. The helicopters also support the cadet parachute team and cadet training missions. The US Naval Test Pilot School received the first of five UH-72As in September 2009. The UH-72A replaced the TH-6B Cayuse as the prime training aircraft for the test pilot school’s helicopter curriculum.
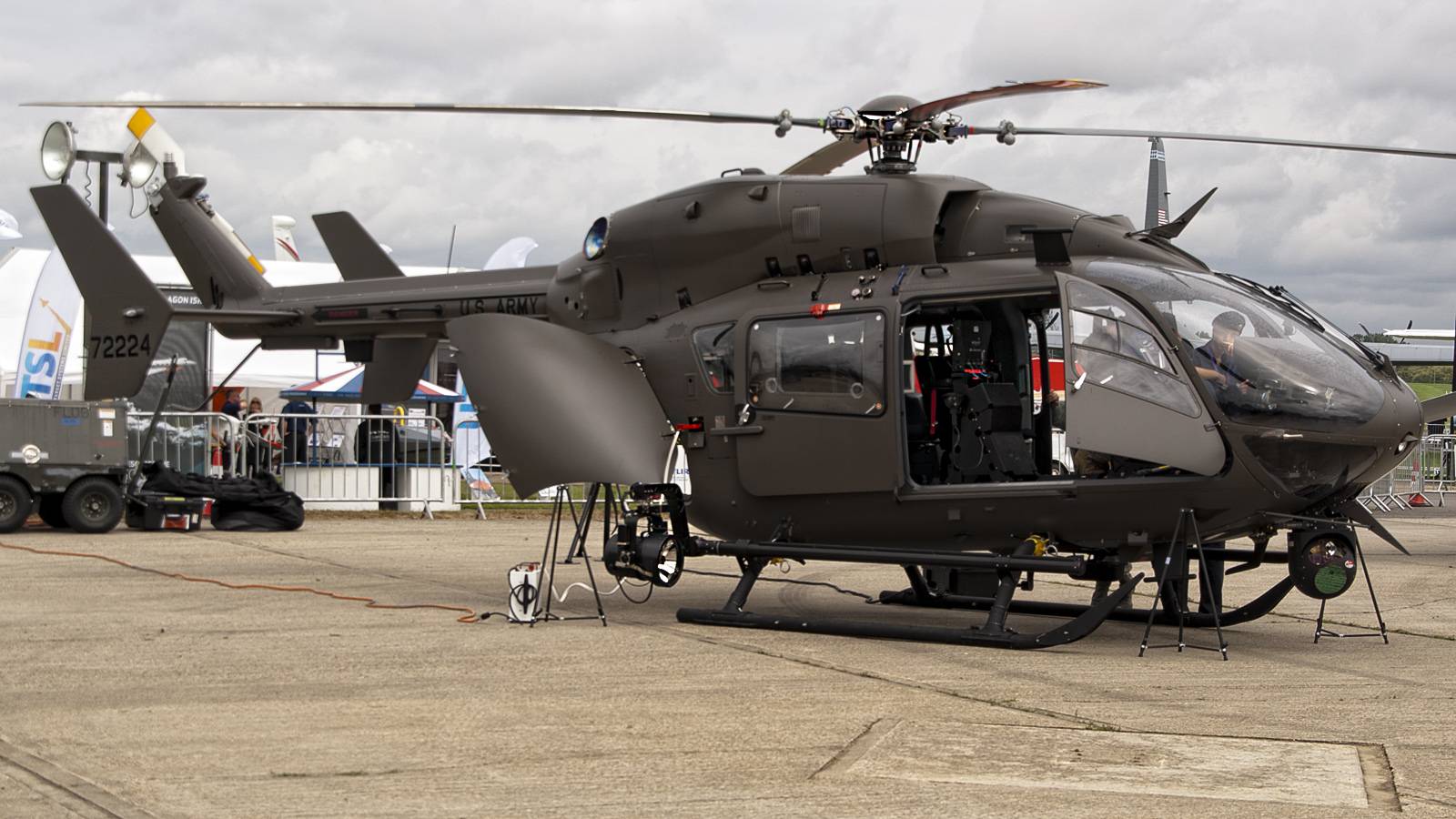
File:UH-72A at Pentagon in 2011.jpg
A UH-72A at the Pentagon, 2010
By March 2010, the Lakota entered service in Puerto Rico, Kwajalein Atoll, and the US Army’s missile test range in Germany. On 20 December 2010, a UH-72A assigned to the Puerto Rico Army National Guard became the first UH-72A to experience a fatal accident. The aircraft crashed at sea off the coast of Puerto Rico and all six personnel aboard were killed.
On 18 July 2012, the US Army’s Aviation Flight Test Directorate received three UH-72As at Redstone Arsenal, Huntsville, Alabama; they are used for general support and as chase aircraft to support aviation development testing. With this delivery, the service has received over 200 UH-72As. On 22 September 2012, the Oregon Army National Guard’s Detachment 1, C Company, 1–112 Aviation, received the first of four UH-72A helicopters during a roll-out ceremony at Camp Rilea in Warrenton, Oregon.
On 25 March 2015, Airbus completed assembly of the first UH-72A made specifically for training for the US Army. The training configuration of the Lakota differs from the baseline model in several ways, including an observer seat for the instructor, a “buzz number” on its side for easy identification, and a flight control system that allows it to communicate with Fort Rucker. As part of the Army’s aviation restructure initiative, Fort Rucker’s fleet of TH-67 training helicopters will be replaced with 187 UH-72s, comprising 106 purpose-built trainers and 81 existing versions that will be modified.
Export
On 7 June 2013, Thailand requested the sale of six UH-72A Lakotas with associated equipment, training, and support for an estimated cost of $77 million. On 9 October 2013, the Thai government approved $55 million in funds to support the Royal Thai Army’s acquisition of six UH-72A helicopters from 2013 to 2015. On 28 March 2014, the Thai Army awarded a $34 million contract to Airbus Helicopter for six UH-72As, fitted with a mission equipment package including the AN/ARC-231 airborne radio terminal; deliveries were to begin by April 2015. On 29 September 2014, Congress was notified of a Thailand request for the sale of another nine UH-72 Lakotas, related equipment, and support. By November 2015, the six helicopters had been delivered.
Background

The US Army’s LHX program began in the early 1980s, proposing two helicopter designs with a high percentage of commonality of dynamic components. One was a light utility version (“LHX-U”) for assault and tactical movement of troops and supplies, the other was a light scout/attack version (“LHX-SCAT”) to complement the growing development of the AH-64 Apache. As the program was developed, the light utility version was dropped and focus was placed on the light attack reconnaissance version, which eventually became the RAH-66 Comanche.

In 2004, the Department of Defense and the US Army made the decision to terminate the RAH-66 program. As part of the termination, the Army retained the future years’ funding intended for the Comanche. To replace the capability of the cancelled Comanche, the US Army planned several programs, including three new aircraft. The Army Staff decided that these three aircraft, the Armed Reconnaissance Helicopter (ARH), the Light Utility Helicopter (LUH), and the Future Cargo Aircraft (FCA) (later renamed Joint Cargo Aircraft, or JCA), were to be existing, in-production commercial aircraft modified for Army service.
Popular books
- Book of Revelation – The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament, and consequently is also the final book of the Christian Bible. Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: apok…
- Book of Genesis – account of the creation of the world, the early history of humanity, Israel’s ancestors and the origins…
- Michelin Guide – Michelin Guides are a series of guide books published by the French tyre company Michelin for more than a century. The term normally refers to the annually published Michelin Red Guide , the oldest…
- Gospel of Matthew – The Gospel According to Matthew is the first book of the New Testament and one of the three synoptic gospels. It tells how Israel’s Messiah, rejected and executed in Israel, pronounces judgement on …
- Ecclesiastes – Ecclesiastes is one of 24 books of the Tanakh , where it is classified as one of the Ketuvim . Originally written c. 450–200 BCE, it is also among the canonical Wisdom literature of the Old Tes…
- Psalms – The Book of Psalms , commonly referred to simply as Psalms , the Psalter or “the Psalms”, is the first book of the Ketuvim , the third section of the Hebrew Bible, and thus a book of th…
- Little Nemo – fictional character created by American cartoonist Winsor McCay. He originated in an early comic strip by McCay, Dream of the Rarebit Fiend , before receiving his own spin-off seri…
Specifications (UH-72A)
Data from UH-72 specifications, Eurocopter EC 145 data
General characteristics
- Crew: 1 or 2 pilots
- Capacity: 9 troops or 2 stretchers and medical crew
- Length: 42 ft 7 in (13.03 m)
- Rotor diameter: 36 ft 1 in (11.0 m)
- Height: 11 ft 9 in (3.45 m)
- Disc area: 1,023 ft2 (94.98 m2)
- Empty weight: 3,951 lb (1,792 kg)
- Useful load: 3,953 lb (1,793 kg)
- Max. takeoff weight: 7,903 lb (3,585 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Turbomeca Arriel 1E2 turboshafts, 738 shp (551 kW) each
Performance
- 145 knots (167 mph, 269 km/h)
- 133 knots (153 mph, 246 km/h)
- Range: 370 nmi (426 mi, 685 km)
- Service ceiling: 13,181 ft (4,018 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,600 ft/min (8.13 m/s)
Sikorsky S-64 Skycrane [1962]
Ну, кто бы мог подумать, что ты сможешь заставить журавля летать? Что ж, это именно то, что имели в виду дизайнеры Sikorsky при проектировании Sikorsky S-64 Skycrane. Построенное как скелет, это странное на вид приспособление может перевозить огромные грузы под своей, казалось бы, хрупкой рамой. На большой площади между его высокими ножками установлен кран, который может с легкостью поднять громоздкий груз весом до 25 000 фунтов (11 300 кг).
Во время войны во Вьетнаме военная версия, обозначенная как CH-54 Tarhe, использовалась для извлечения более 380 сбитых военных самолетов. Это сэкономило миллионы долларов, поскольку делать то же самое с использованием других методов было намного дороже. Он также использовался для перевозки танков, грузовиков и войск. Еще одно уникальное применение заключалось в переноске универсальных военных контейнеров-капсул, которые могли быть адаптированы для таких целей, как хирургические отделения, в зависимости от требований.
Гражданская версия построила несколько тысяч миль линий электропередачи. Вертолет доказал свою полезность благодаря своей способности устанавливать опоры линий электропередачи в самых разнообразных условиях местности. Противопожарная версия имеет емкость 2650 галлонов (10 000 литров) воды и используется при тушении лесных пожаров. Еще одно популярное применение этого вертолета – лесозаготовки. Да, вы все правильно расслышали. Огромная грузоподъемность, предлагаемая Skycrane, делает его выгодным вариантом для перевозки бревен из труднодоступных лесов обратно в цивилизацию для переработки. В настоящее время он остается единственным в своем роде, не имеет конкуренции на рынке и все еще находится в производстве.
Specifications (UH-72A)
Data from UH-72 specifications, Eurocopter EC 145 data
General characteristics
Crew: 1 or 2 pilots
Capacity: 9 troops or 2 stretchers and medical crew
Length: 42 ft 7 in (13.03 m)
Rotor diameter: 36 ft 1 in (11.0 m)
Height: 11 ft 9 in (3.45 m)
Disc area: 1,023 ft2 (94.98 m2)
Empty weight: 3,951 lb (1,792 kg)
Useful load: 3,953 lb (1,793 kg)
Max. takeoff weight: 7,903 lb (3,585 kg)
Powerplant: 2 × Turbomeca Arriel 1E2 turboshafts, 738 shp (551 kW) each
Performance
Maximum speed: 145 knots (167 mph, 269 km/h)
Cruise speed: 133 knots (153 mph, 246 km/h)
Range: 370 nmi (426 mi, 685 km)
Service ceiling: 13,181 ft (4,018 m)
Sikorsky S-97 Raider [2015]
Хотя он не находится на вооружении вооруженных сил США, этот список был бы неполным без невероятного Sikorsky S-97 raider. Построенный в соответствии с будущими требованиями армии США к вооруженному воздушному разведчику, Raider включает в себя множество новых технологий, которые позволяют ему преуспеть на поле боя и превзойти своих конкурентов. Наиболее заметной особенностью вертолета является его соосная несущая система, которая обычно используется на российских вертолетах Камова, и толкающий винт. Эта конструкция обеспечивает значительное улучшение по сравнению с обычной конструкцией вертолета, поскольку энергия не тратится впустую, пытаясь противодействовать вращению несущего винта с помощью рулевого винта. Вместо этого соосные несущие винты компенсируют крутящий момент друг друга и обеспечивают необходимую подъемную силу, в то время как толкающий винт обеспечивает переднюю тягу, что дает ему дополнительный толчок, необходимый для полета быстрее, чем его современники.
Рейдер может вместить 6 военнослужащих и нести ракетные капсулы под обрубками крыльев для обеспечения огневой поддержки. Максимальная скорость, которую он может развивать, составляет 444 км / ч, что позволит ему быстро входить и выходить из враждебных районов во время разведывательной или десантной миссии. Этот конкретный вертолет предназначен для спецназа США, поскольку он может быть полезен для быстрой переброски и эвакуации войск. Поступит ли он на самом деле на вооружение вооруженных сил США или нет, остается предметом спекуляций, но этот дизайн определенно будет усовершенствован, и мы увидим похожие вертолеты в ближайшие десятилетия.
#топ 10 #технологии #история #исторические факты #сша #военные #военный #техника #соединенные штаты америки #военная техника
Boeing AH-64 Апач [1975]
Широко признанный как самый совершенный ударный вертолет, находящийся на вооружении сегодня, Апач составляет основу наземных операций вооруженных сил США на протяжении более 3 десятилетий. Он был разработан в качестве замены AH-1 в армии США. В попытке сделать его живучим на опасном поле боя, Апач имеет броню, которая позволяет ему выдерживать попадания из 23-мм зенитных орудий, и самоуплотняющийся топливный бак, который предотвращает утечку топлива в случае попадания в танк.
Вооруженный 16 ракетами Хеллфайр, Апач – это идеальный истребитель. Эти усовершенствованные ракеты управляются лазером и могут уничтожать цели на расстоянии более 5 миль. В качестве альтернативы он может нести ракетные капсулы для поражения небронированных целей. Под носом находится 30-мм пушка, которая может стрелять со скоростью 300 выстрелов в минуту. Также могут быть установлены ракеты Стингер, которые позволяют Апачу уничтожать серийные цели. В конце 90-х годов был установлен радар longbow, который позволял Апачу уничтожать цели из-за укрытия, не подвергая себя воздействию противника. Таким образом, вертолет представляет собой универсальную систему вооружения, которая может сеять хаос на поле боя.
Operational history
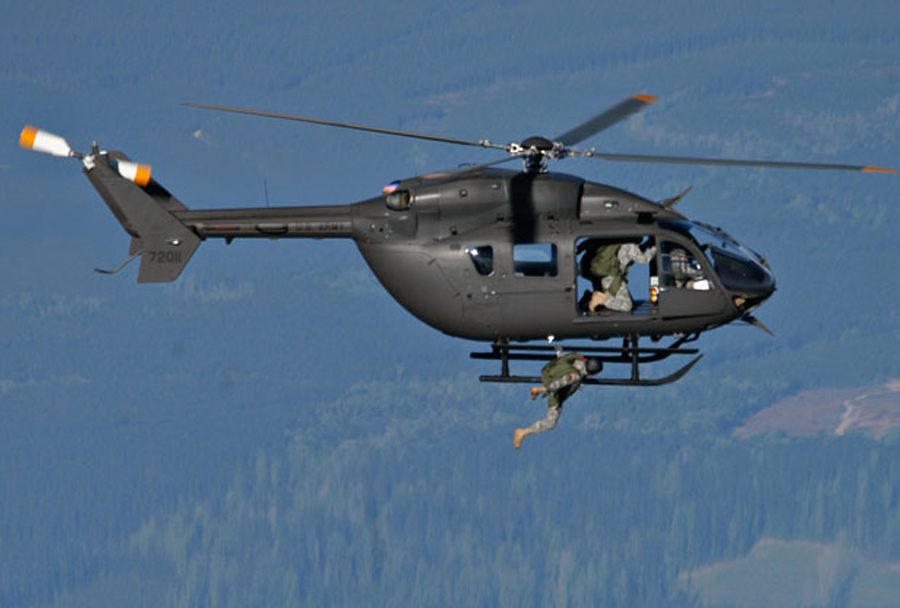
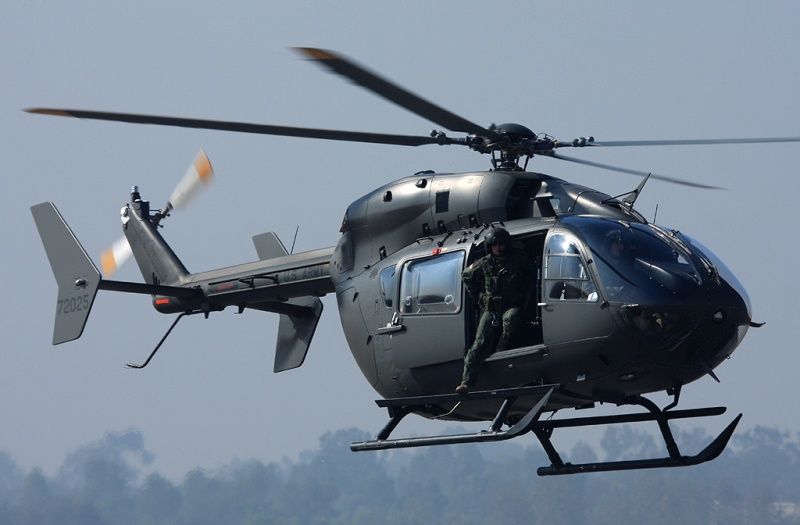
A UH-72 of 2916th BN provides air support to OPFOR units of the 11th ACR.
The first aircraft was delivered to the US Army on 11 December 2006 in Columbus, Mississippi. On 12 December 2006, General Richard A. Cody, Vice Chief of Staff of the Army, and Joe Red Cloud, a chief of the Oglala Sioux Tribe, Lakota nation, accepted the first UH-72A in an official ceremony. The service estimated that delivery of the planned 345 aircraft would continue until 2017.
The first production helicopters were sent to the National Training Center (NTC), Fort Irwin, California for medical evacuation missions in January 2007. On 20 June 2007, the NTC’s US Army Air Ambulance Detachment (USAAAD) became the first operational unit to field the Lakota. On 10 July 2007, the Training and Doctrine Command (TRADOC) Flight Detachment at Fort Eustis, Virginia became the second US Army unit fielded with the UH-72A.
A report published in August 2007 by the Operational Test and Evaluation Directorate (DOT&E) noted that although the Lakota “…is effective in the performance of light utility missions,” it was prone to overheating during operations in the desert conditions of Fort Irwin when not equipped with air conditioning systems. In response, vents were added in the doors to increase cabin air flow; air conditioning has been installed on some Medical and VIP versions, as well as added air conditioning units for crew comfort.
The (JRTC) located at Fort Polk, Louisiana received their first aircraft on 7 September 2007. On 16 January 2009, the United States Military Academy received two UH-72As, replacing two UH-1H helicopters for VIP transport to and from the academy. The helicopters also support the cadet parachute team and cadet training missions. The US Naval Test Pilot School received the first of five UH-72As in September 2009. The UH-72A replaced the TH-6B Cayuse as the prime training aircraft for the test pilot school’s helicopter curriculum.
The first two Army National Guard UH-72As at Tupelo, Mississippi
By March 2010, the Lakota entered service in Puerto Rico, Kwajalein Atoll, and the US Army’s missile test range in Germany. On 20 December 2010, a UH-72A assigned to the Puerto Rico Army National Guard became the first UH-72A to experience a fatal accident. The aircraft crashed at sea off the coast of Puerto Rico and all six personnel aboard were killed.
On 18 July 2012, the US Army’s Aviation Flight Test Directorate received three UH-72As at Redstone Arsenal, Huntsville, Alabama; they are used for general support and as chase aircraft to support aviation development testing. With this delivery, the service has received over 200 UH-72As. On 22 September 2012, the Oregon Army National Guard’s Detachment 1, C Company, 1–112 Aviation, received the first of four UH-72A helicopters during a roll-out ceremony at Camp Rilea in Warrenton, Oregon.
On 25 March 2015, Airbus completed assembly of the first UH-72A made specifically for training for the US Army. The training configuration of the Lakota differs from the baseline model in several ways, including an observer seat for the instructor, a “buzz number” on its side for easy identification, and a flight control system that allows it to communicate with Fort Rucker. As part of the Army’s aviation restructure initiative, Fort Rucker’s fleet of TH-67 training helicopters will be replaced with 187 UH-72s, comprising 106 purpose-built trainers and 81 existing versions that will be modified.
In 2018, the 1–376th AVN BN was deployed to Germany with UH-72A Lakotas supporting MEDEVAC missions at Hohenfels and Grafenwoehr military bases. The Lakotas took over the mission from 214th Aviation Battalion Black Hawks; this is the first deployment of the Lakota outside the US. citation needed
Contractors involved
EADS North America selected companies such as LCX Systems, Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC), Ranger Rotorcraft Group, MARK IV Luminator, and L-3 Communications (now L3Harris) for the security and support mission equipment package. The package includes an electro-optical infrared sensor, a data communications suite, moving map display, cabin and cockpit screens, a digital video recorder and a searchlight.
Sikorsky was contracted to supply the UH-72A logistic support, including maintenance contract management, supply chain management, contractor field teams, spare part and tool management, facilities management and field and depot-level maintenance.
Safran Electronics & Defense, Avionics was selected to provide avionics systems for the UH-72A helicopters.
CH-53 Сталлион [1964]
Это самый большой вертолет на вооружении США. При грузоподъемности более 14 000 фунтов (6350 кг) для начальной двухмоторной версии он мог перевозить эквивалентный вес 4 взрослых носорогов. Американские военные используют этот вертолет для транспортировки войск, высадки спецназа, эвакуации раненых и подъема тяжелых транспортных средств, таких как грузовики. CH-53, будучи преимущественно морским вертолетом, имеет водонепроницаемый корпус, который позволяет ему безопасно приземляться на воду в чрезвычайной ситуации. Самые ранние варианты поступили на вооружение во время войны во Вьетнаме, а самый последний вариант теперь поступит в производство. Это еще раз доказывает долговечность американских вертолетных конструкций.
Его самая уникальная роль – это роль сапера! Мощный трехмоторный вариант MH-53 может нести полезную нагрузку весом 32 000 фунтов (14 500 кг), что позволяет ему буксировать за собой тральные сани по поверхности моря. Это позволяет вертолету обезвреживать мины быстрее и безопаснее, чем тральщику. Последней версией является трехмоторный CH-53K Сталлион, который изготовлен из более легких композитных материалов и оснащен мощными двигателями, которые позволяют ему нести полезную нагрузку в 35 000 фунтов (15 800 кг), что более чем в 2 с половиной раза превышает полезную нагрузку первоначальной версии. Сталлион составит основу тяжеловесных сил USMC и останется на вооружении в ближайшие десятилетия.
Popular articles
- 2022 FIFA World Cup – The 2022 FIFA World Cup is scheduled to be the 22nd edition of the FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial international men’s association football championship contested by the national teams of the member…
- FIFA World Cup – international association football competition contested by the senior men’s national teams of the members of the Fédération Interna…
- Cristiano Ronaldo – Portuguese professional footballer who plays as a forward for club Juventus and captains the Portugal national team. Often considered the best player in the …
- Guillermo Ochoa – Mexican professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper for Liga MX club América and the Mexico national team. Ochoa made h…
- Qatar – country located in Western Asia, occupying the small Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Its sole land border is with nei…
- Hervé Renard – French football coach and former professional player who is manager of Saudi Arabia. He has previously been the manager of the Zambian national team, with whom he won the 2012 Afr…
- Saudi Arabia national football team – The Saudi Arabia national football team represents Saudi Arabia in men’s international football and The team’s colours are green and white. Saudi Arabia are known as Al-Suqour and Al-Akhdhar , Th…
Navigation, communications and cabin of UH-72A
UH-72A Lakota light utility helicopter’s navigation and communications systems were supplied by Wulfsberg Electronics based in Prescott, Arizona. The navigation and air traffic control communications include dual VHF communications transceivers, dual VHF navigation receivers with VOR, ILS and marker beacon, and a DME transceiver.
The UH-72A’s tactical communications system includes an RT-5000 wideband transceiver operating at 29MHz to 960MHz, and dual P-2000 tactical communications transceivers. Wulfsberg Electronics also supplies navigation and communications systems for EC145 helicopters used in civilian and special mission roles.
The cabin accommodates eight troops or passengers. The cabin is fitted with BAE System’s Simula passenger seats which are of fold-up design and meet FAA crashworthiness standards. The cockpit and passenger seats are of high strength, lightweight composites construction and include aramid and graphite materials.
The cockpit and cabin are fitted with a heating and ventilating system supplied by Keith Products. The Keith Products heating, ventilation and cooling systems are fitted as standard equipment for all civilian EC145 versions of the Lakota UH-72A.






![Еврокоптер uh-72 lakotaсодержание а также развитие [ править ]](https://gunsfriend.ru/wp-content/uploads/d/4/8/d487beba4f57c125f2a651682fdf2428.png)