История[ | ]
Разработка управляемой ракеты Х-59 выполнялась МКБ «Радуга». Лётно-конструкторские испытания ракет X-59 «Овод» проведены в 1975—1977 годах в ГЛИЦ (Ахтубинск).
Государственные испытания X-59 были закончены в 1979, на вооружение комплекс в составе истребителя-бомбардировщика Су-24М, контейнера управления и двух ракет Х-59 был принят в 1980 году. Также, «Оводом» оснащались одноместные истребители-бомбардировщики Су-17М, такой комплекс получил наименование Су-17М4. Х-59 в составе Су-17М4 был принят на вооружение в 1982 году, но, из-за прекращения серийного выпуска Су-17, основным носителем Х-59 являлся Су-24М.
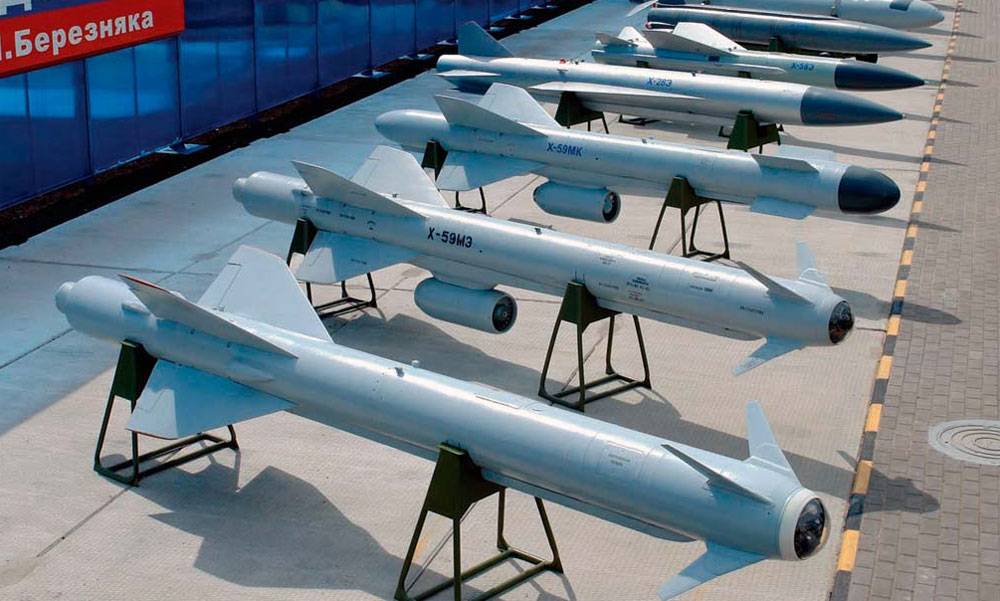
Сейчас модификации Х-59 производятся и модернизируются корпорацией «Тактическое ракетное вооружение» в которую входит МКБ «Радуга».
Design
The original Kh-59 is propelled by a solid fuel engine, and incorporates a solid fuel accelerator in the tail. The folding stabilizers are located in the front of the missile, with wings and rudder in the rear. The Kh-59 cruises at an altitude of about 7 metres above water or 100–1,000 metres (330–3,280 ft) above ground with the help of a radar altimeter. It can be launched at speeds of 600 to 1,000 km/h (370 to 620 mph) at altitudes of 0.2 to 11 kilometres (660 to 36,090 ft) and has a CEP of 2 to 3 metres. It is carried on an AKU-58-1 launch pylon.
The Kh-59ME has an external turbofan engine below the body just forward of the rear wings, but retains the powder-fuel accelerator. It also has a dual guidance system consisting of an inertial guidance system to guide it into the target area and a television system to guide it to the target itself.
The 36MT turbofan engine developed for the Kh-59M class of missiles is manufactured by NPO Saturn of Russia.
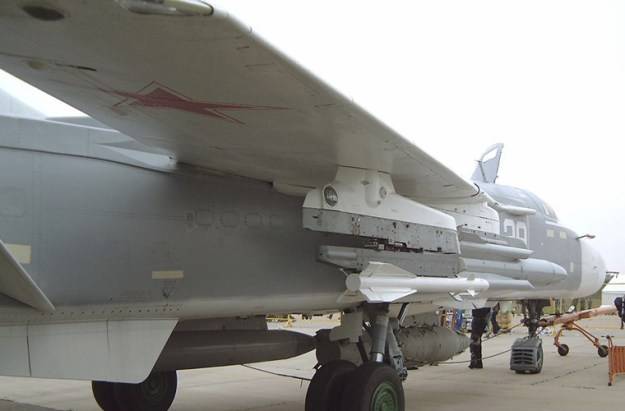
Kh-29L air-to-surface missiles (AS-14 Kedge)
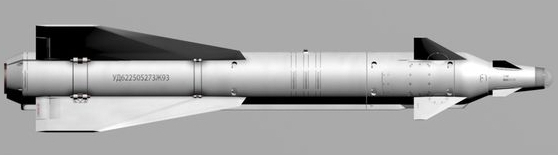
The Kh-29L air-to-surface missiles are designed to engage visually observed hardened ground and surface targets, such as big railway and highway bridges, industrial installations, concrete runways, aircraft in reinforced concrete shelters, surface vessels displacing up to 10,000 tonnes. Kh-29L is equipped with a semi-active laser guidance system using reflected laser illumination spot.
The missiles are armed with a high explosive penetrating warhead and an impact target sensor. They are powered by a single-mode solid-fuel rocket engine.The missiles make part of weapon systems of multi-role fighters and attack aircraft.
Designed: Soviet Union 1975 (X-29)
Manufacturer: Vympel
Weight: 660 kgs
Length: 390 cm
Diameter: 38 cm
Warhead: HE Armour-piercing
Warhead weight: 320 kgs
Detonation mechanism : Impact
Engine: Fixed thrust solid fuel rocket
Wingspan: 110 cm
Op. range min/max: 3-10 km
Speed: 1,470 km/h (910 mph)
Guidance System: semi-active Laser guidance
Source
Ljulka AL-21 F 3
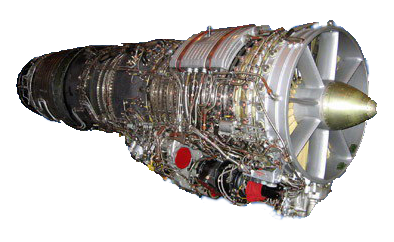 Image motor-lutsk.com.ua
Image motor-lutsk.com.ua
SPECIFICATIONS:
| Rf (thrust in afterburner mode) | 11215 kgs |
| Rmah (traction at maximum capacity) | 7800 kgs |
| Tr (gas temperature before the turbine) | 1097 ° C |
| The degree of pressure increase | 14.5 |
| engine weight | 1800 kg |
| Air consumption | 104 kg / s |
| The diameter of the engine | 1030 mm |
| engine Length | 5340 mm |
Installed on the aircraft Su-17, Su-20, Su-22, Su-24
Engine data motor-lutsk.com.ua
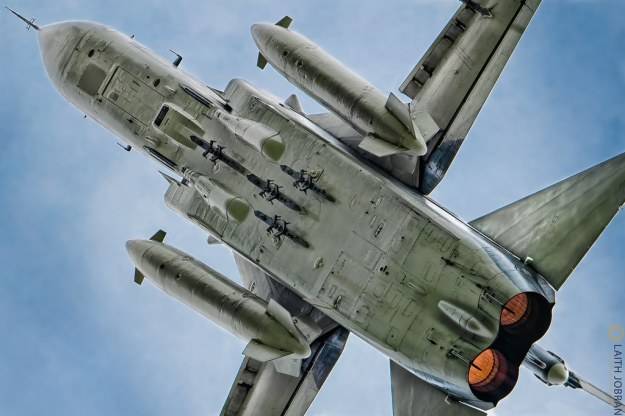

Laith Jobran @flickr
An inert gas system is installed for fire safety. The Su-24M aircraft is equipped with a flight refuelling system.
The Su-24M has a maximum speed of 1,550km/h and a range of over 3,000km. The service ceiling is 11,000m and the maximum rate of climb is 9,000m a minute.
Main material source airforce-technology.com
Update Aug 06, 2018
| Technical sheet | |||
| Su-24 | Su-24M | Su-24MR | |
| Length | 22.67 m | 22,59 m | 20.53 m |
| Wingspan (wings) | 17.64 m | 17.64 m | 17.64 m |
| Ground clearance | 5.92 m | 5.92 m | 5.92 m |
| Wing area (wings) | 55,16 m 2 | 55,16 m 2 | 55,16 m 2 |
| Empty weight | 21,150 kg | 22,300 kg | 22,100 kg |
| MTOW | 39,700 kg | 39,700 kg | 39,700 kg |
| Crew | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| motorization | 2 AL-21F turbofan Lioulka-3 11 200 kp each with afterburner | 2 AL-21F turbofan Lioulka-3 11 200 kp each with afterburner | 2 AL-21F turbofan Lioulka-3 11 200 kp each with afterburner |
| operational ceiling | 17 000 m | 17 000 m | 17 000 m |
| Maximum speed | 1700 km / h | 1700 km / h | 1430 km / h |
| stop range | 3055 km with additional tanks | 2850 km with additional tanks | 2500 km with additional tanks |
| take-off roll | 900 m | 1250m | 1200 m |
| Landing roll | 800 m with parachute | 950 m with parachute | 1000 m with parachute |
| armament | 1 sextuple gun hCG-6-23 23 mm (500 rounds) up to 7000 kg of external loads | 1 sextuple gun hCG-6-23M 23 mm (500 rounds) up to 8000 kg of external loads | 2 air-air missile R-60 or R60M |
Technical data krasnayazvezda.com
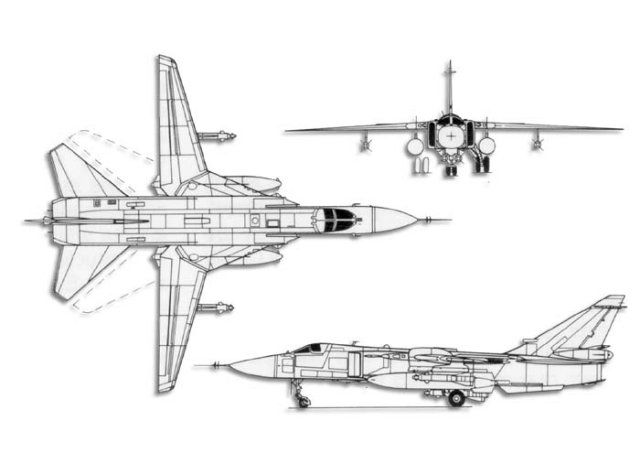 Image airrecognition.com
Image airrecognition.com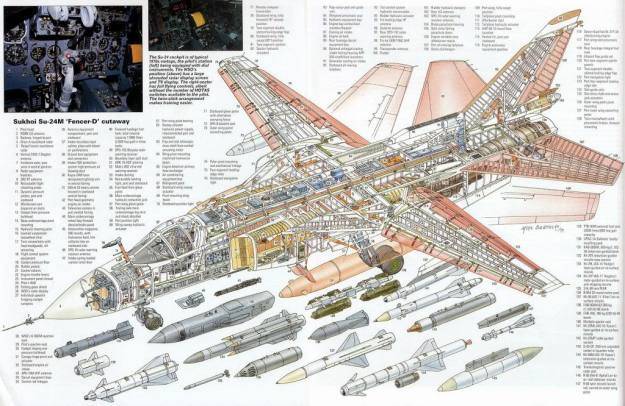
Применение
Тактика применения:
Чеченская война (1994—1996) и (1999—2000)
Ракеты Х-59М использовались в ходе боевых действий в Чечне для уничтожения укрытий и складов боевиков в горах. Климат Северного Кавказа наложил серьёзные ограничения на применение высокоточного оружия — плохие метеоусловия, туман и слабая видимость приводили к срыву наведения в лесистых горах и заснеженных ущельях. Например, за весь декабрь 1994 года в Чечне было всего 2 дня с ясной погодой, когда было возможно использовать все возможности высокоточного оружия. От применения ракет Х-59 отказались после четырёх пусков.
Operational history
Although the original Kh-59 could be carried by the MiG-27, Su-17M3, Su-22M4, Su-24M, Su-25 and Su-30 family if they carried an APK-9 datalink pod, it was only fielded on the Su-24M in Russian service. From 2008–2015, Russia delivered some 200 Kh-59 missiles to China for use on the Su-30MK2; deliveries may have included both Kh-59MK and Kh-59MK2 versions. The Kh-59MK2 has been test-fired by a Su-57 stealth fighter, during its 2018 Syrian deployment.
On 4 April 2022, during the Russian invasion of Ukraine, photographic evidence was published on Telegram channels that a Kh-59M missile was launched by the Russian Air Force at a grain silo near Mykolaiv, Ukraine. The missile was captured on CCTV as it was traveling to the target area.
Vympel R-60 (AA-8 Aphid)
The Molniya (now Vympel) R-60 (NATO reporting name: AA-8’Aphid’) is a short-range lightweight infrared homing air-to-air missile designed for use by Soviet fighter aircraft. It has been widely exported, and remains in service with the CIS and many other nations.
| Type | Short-range air-to-air missile |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1974- present |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Vympel |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 43.5 kg (96 lb) |
| Length | 2,090 mm (6 ft 10 in) |
| Diameter | 120 mm (4.7 in) |
| Warhead | 3 kg (6.6 lb) |
| Detonation mechanism | proximity |
| Engine | solid-fuel rocket engine |
| Wingspan | 390 mm (15 in) |
| Operational range | 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) |
| Flight altitude | 20,000 m (66,000 ft) |
| Speed | Mach 2.7 |
| Guidance system | infrared homing |
Source wikiwand.com
ruforces (flickr)
The Su-24M aircraft is armed with: Kh-25L (AS-10 Karen) laser-guided missiles (range 20km; up to four missiles carried); Kh-29LT (AS-14 Kedge) laser / TV-guided missiles (range 10km; up to three missiles carried); Kh-31P (AS-17 Krypton) passive radar-homing missiles (range 180km; up to two missiles carried); and Kh-59 (AS-13 Kingbolt) TV-command-guided missiles (range 90km; up to two missiles carried).
Introducing the SVP-24:
SVP stands for “специализированная вычислительная подсистема” or “special computing subsystem”. What this system does is that it constantly compares the position of the aircraft and the target (using the GLONASS satellite navigation system), it measures the environmental parameters (pressure, humidity, windspeed, speed, angle of attack, etc.). It can also receive additional information from datalinks from AWACs aircraft, ground stations, and other aircraft. The SVP-24 then computes an “envelope” (speed, altitude, course) inside which the dumb bombs are automatically released exactly at the precise moment when their unguided flight will bring them right over the target (with a 3-5m accuracy).

In practical terms this means that every 30+ year old Russian “dumb” bomb can now be delivered by a 30+ year old Russian aircraft with the same precision as a brand new guided bomb delivered by a top of the line modern bomber.
Not only that, but the pilot does not even have to worry about targeting anything. He just enters the target’s exact coordinates into his system, flies within a defined envelope and the bombs are automatically released for him. He can place his full attention on detecting any hostiles (aircraft, missiles, AA guns). And the best part of this all is that this system can be used in high altitude bombing runs, well over the 5000m altitude which MANPADs cannot reach. Finally, clouds, smoke, weather conditions or time of the day play no role in this whatsoever.
Last, but not least, this is a very *cheap* solution. Russian can now use the huge stores of ‘dumb’ bombs they have accumulated during the Cold War, they can bring an infinite supply of such bombs to Syria and every one of them will strike with phenomenal accuracy. And since the SVP-24 is mounted on the aircraft and not the bomb, it can be reused as often as needed.
The SVP-24 has now been confirmed to be mounted on the Russian SU-24s, SU-25s, Tu-22M3 “Backfires” and the Kamov Ka-50 and Ka-52 helicopters, the venerable MiG-27 and even the L-39 trainer. In other words, it can be deployed on practically *any* rotary or fixed wing aircraft, from big bombers to small trainers. I bet you the Mi-24s and Mi-35Ms deployed near Latakia also have them.






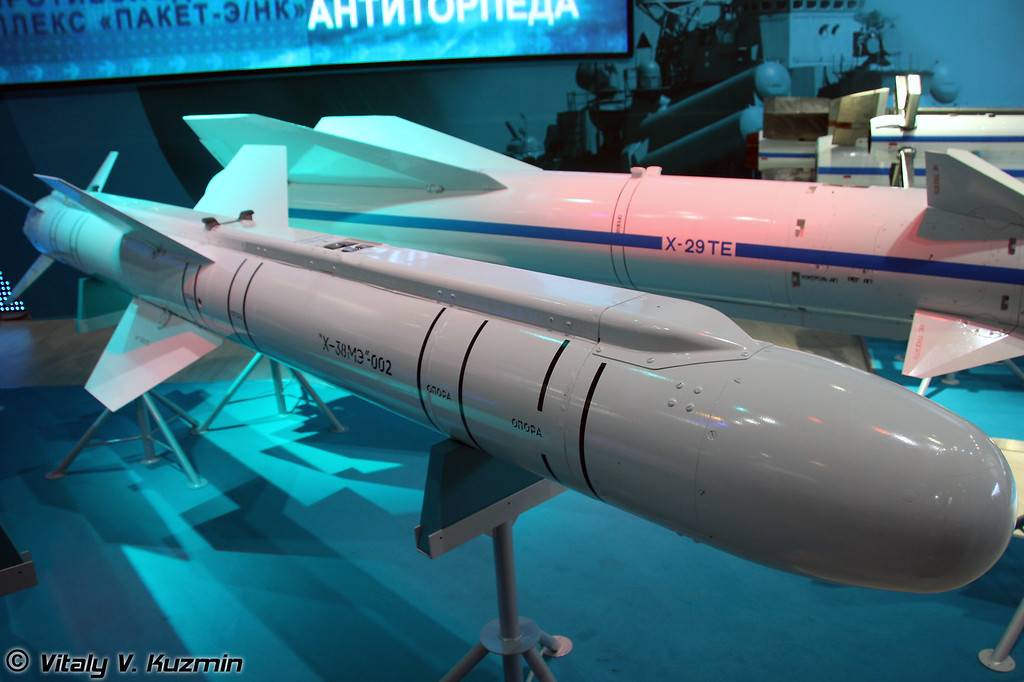
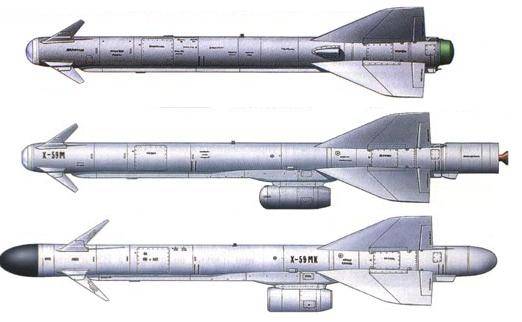
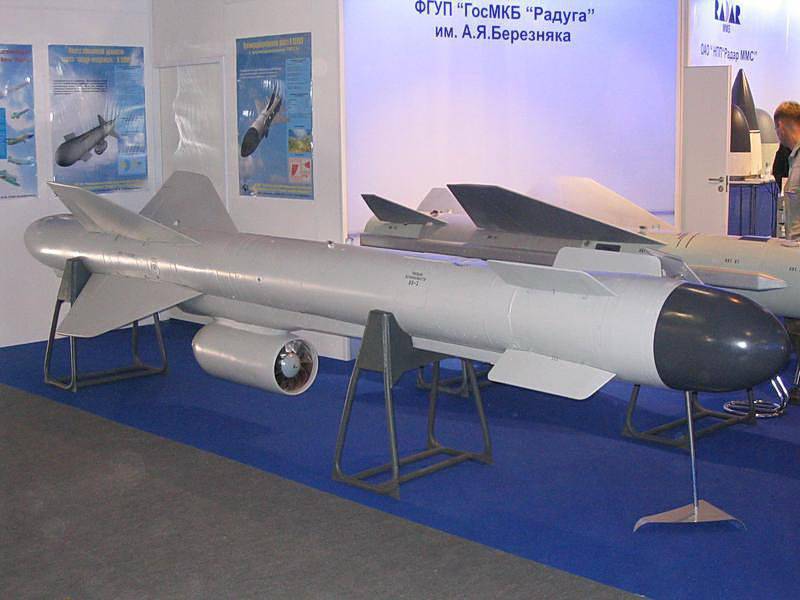
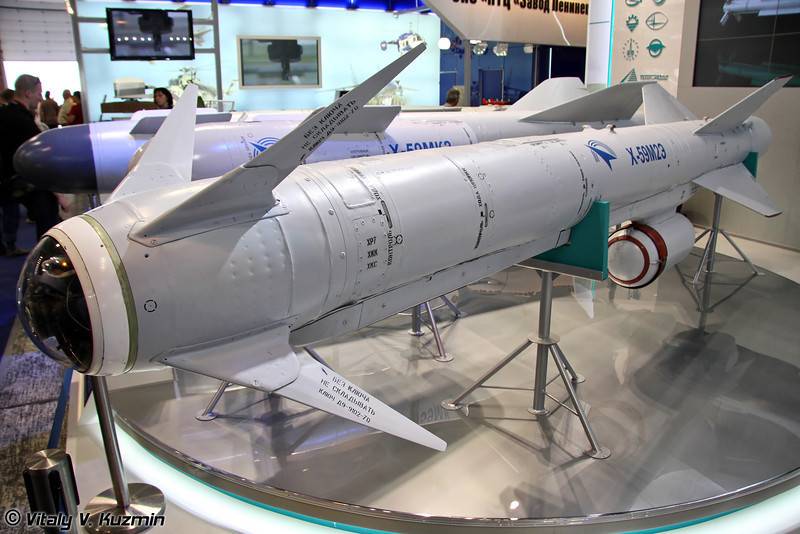
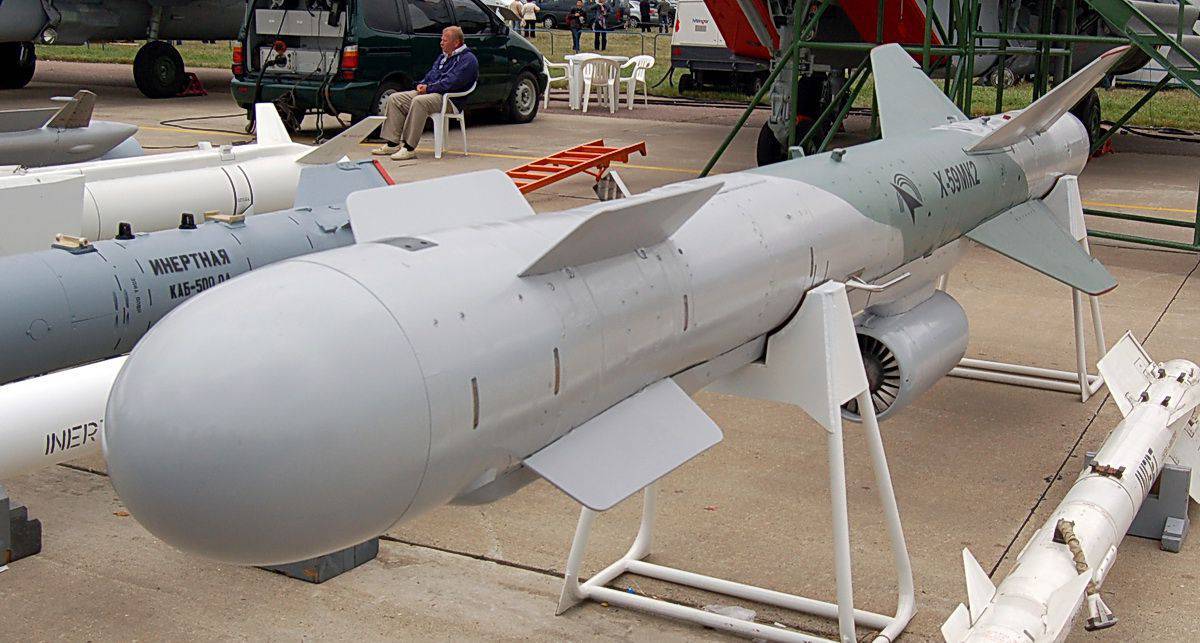
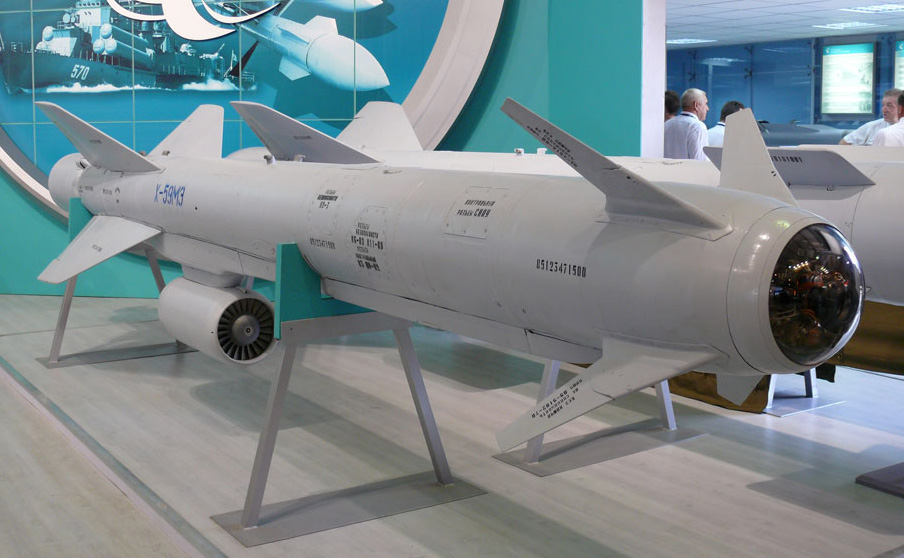
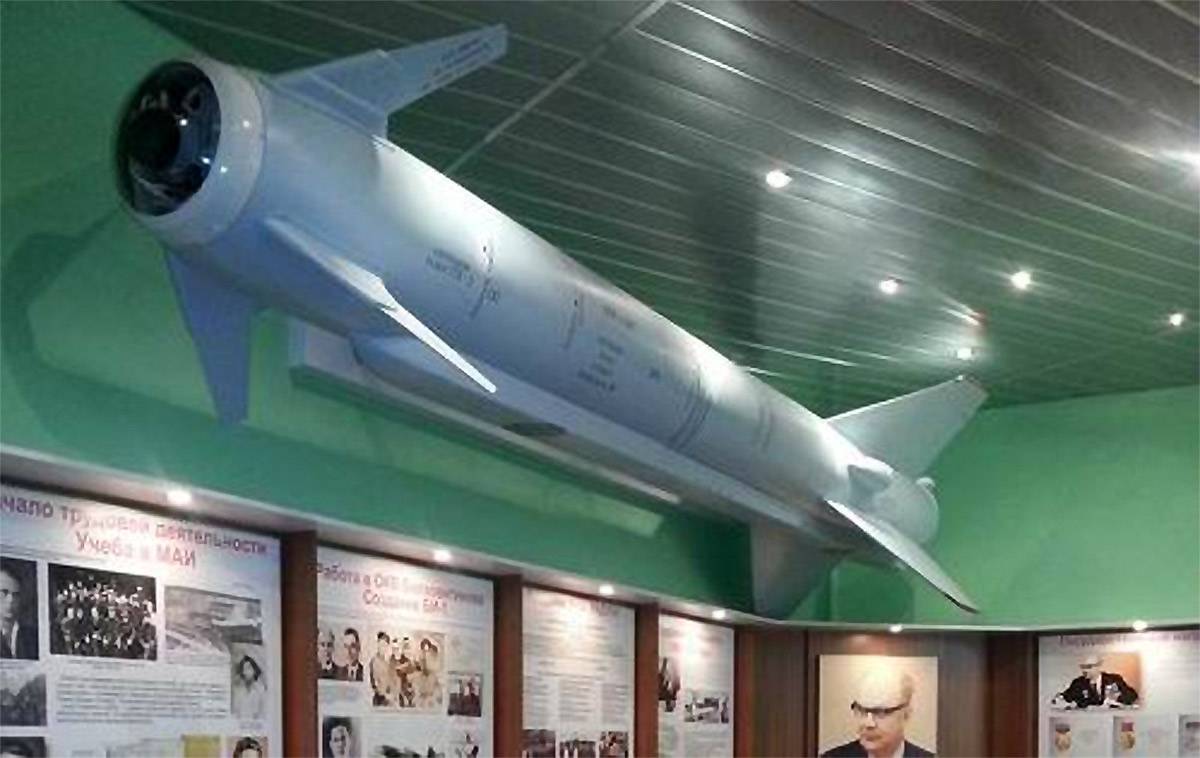
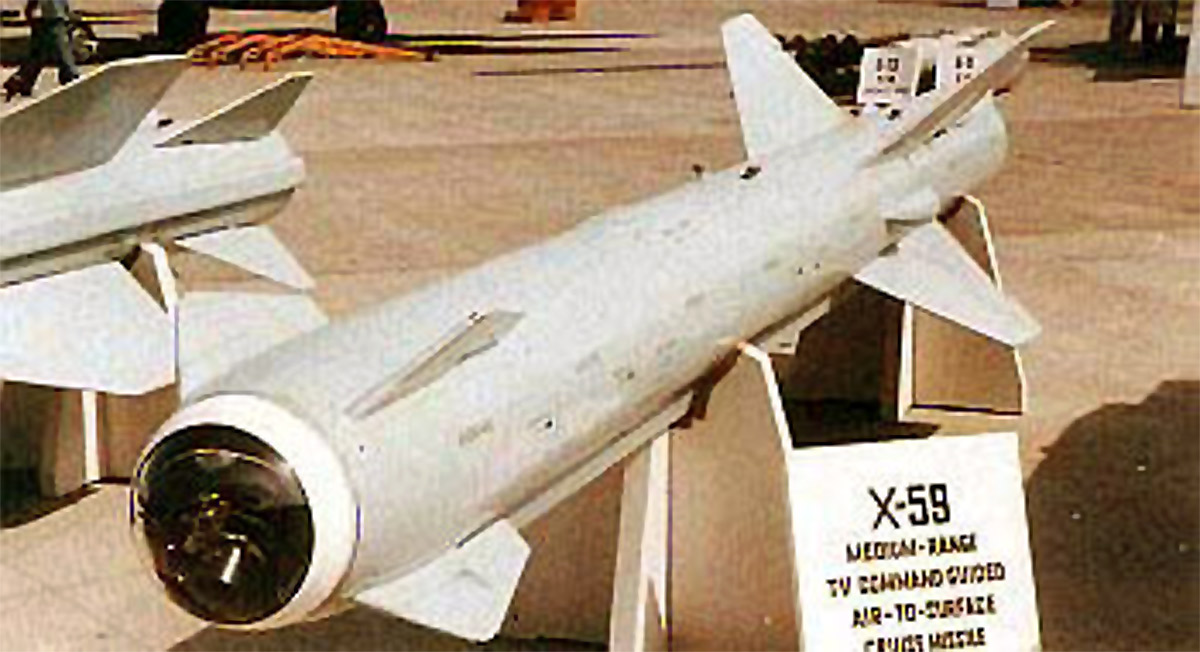
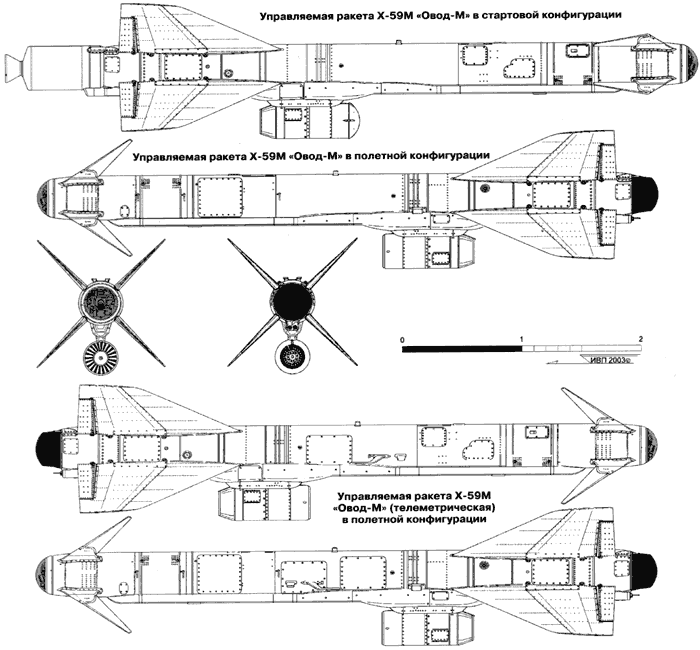
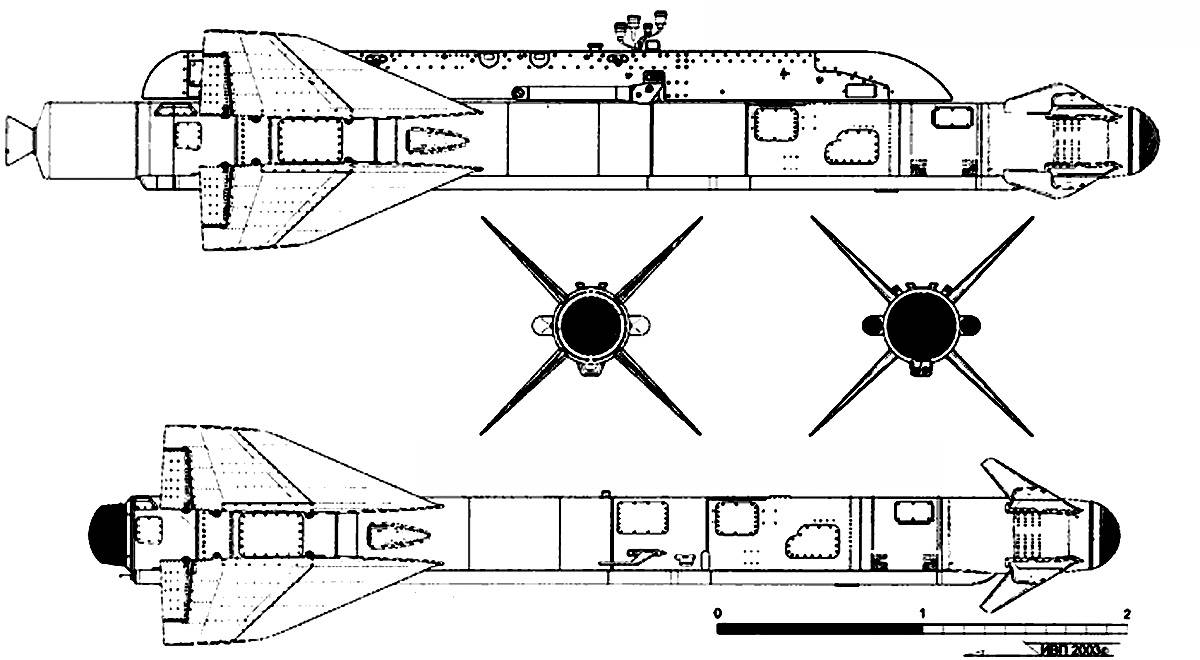
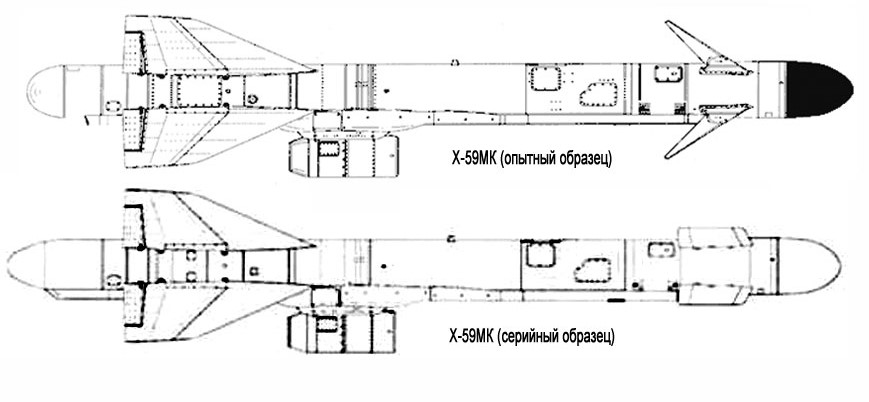
Kh-59 (AS-13 Kingbolt)

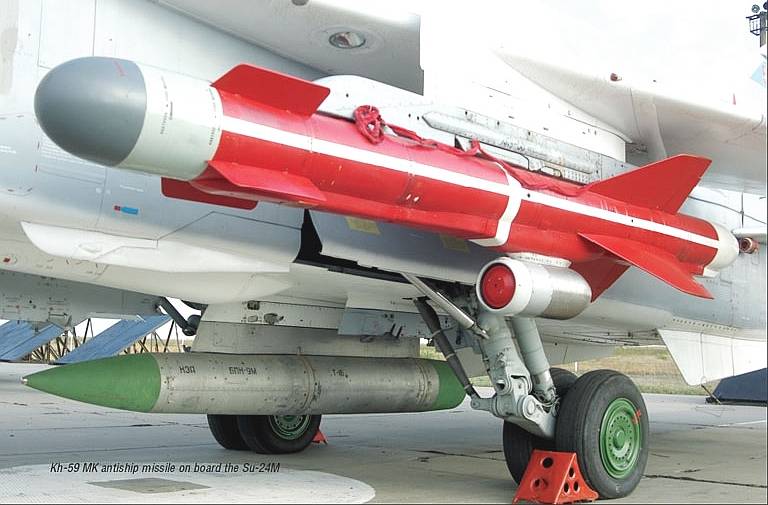
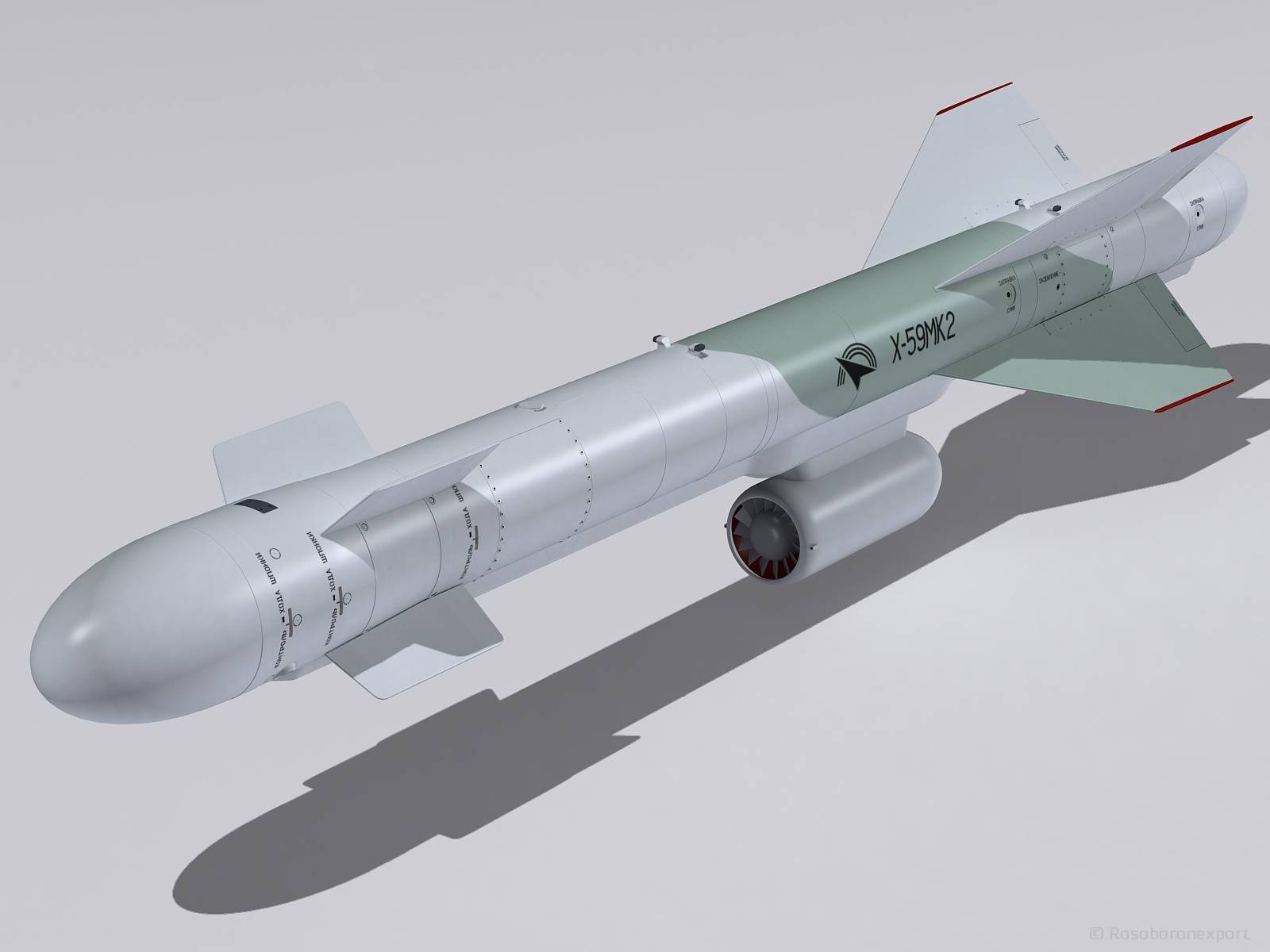
The Kh-59 Ovod (Russian: Х-59 Овод ‘Gadfly’; AS-13 ‘Kingbolt’) is a Russian TV-guided cruise missile with a two-stage solid-fuel propulsion system and 200 km range. The Kh-59M Ovod-M(AS-18 ‘Kazoo’) is a variant with a bigger warhead and turbojet engine. It is primarily a land-attack missile but the Kh-59MK variant targets shipping.
APK-9 datalink pod for the Kh-59M
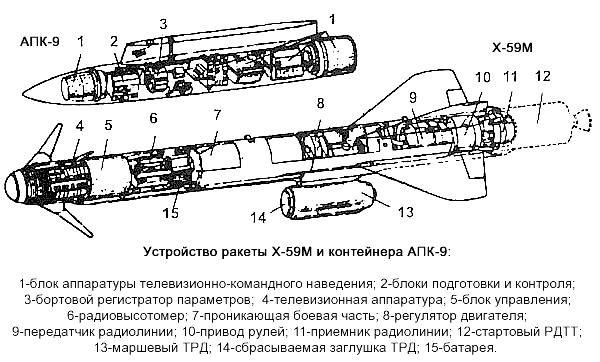
 APK-9 Tekon pod –Image @ausairpower.net
APK-9 Tekon pod –Image @ausairpower.net
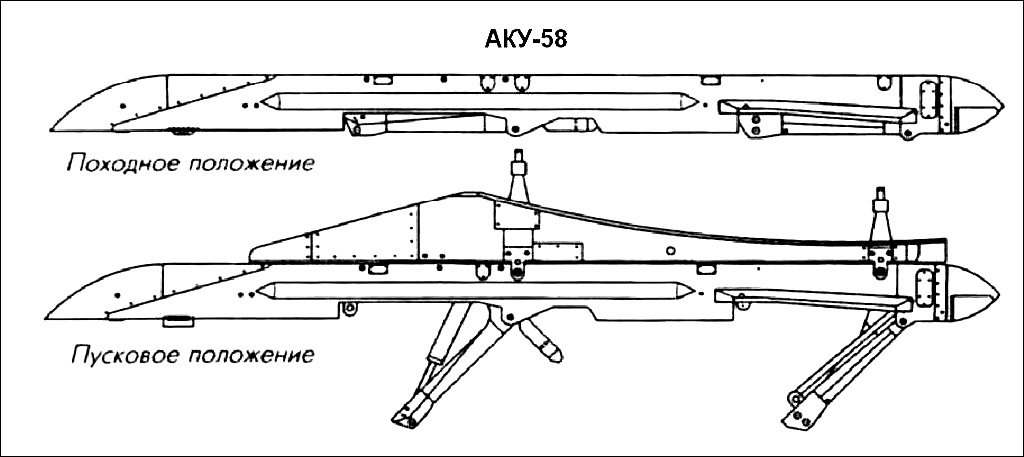
The original Kh-59 is propelled by a solid fuel engine, and incorporates a solid fuel accelerator in the tail. The folding stabilizers are located in the front of the missile, with wings and rudder in the rear. The Kh-59 cruises at an altitude of about 7 meters above water or 100–1,000 metres (330–3,280 ft) above ground with the help of a radar altimeter. It can be launched at speeds of 600 to 1,000 km/h (370 to 620 mph) at altitudes of 0.2 to 11 kilometres (660 to 36,090 ft) and has a CEP of 2 to 3 meters. It is carried on an AKU-58-1 launch pylon.
The Kh-59ME has an external turbofan engine below the body just forward of the rear wings, but retains the powder-fuel accelerator. It also has a dual guidance system consisting of an inertial guidance system to guide it into the target area and a television system to guide it to the target itself.
The 36MT turbofan engine developed for the Kh-59M class of missiles is manufactured by NPO Saturn of Russia.
36MT turbofan engine
Design features
1-stage fan
axial-diagonal high pressure compressor
annular combustor
1-stage high pressure turbine
1-stage low pressure turbine
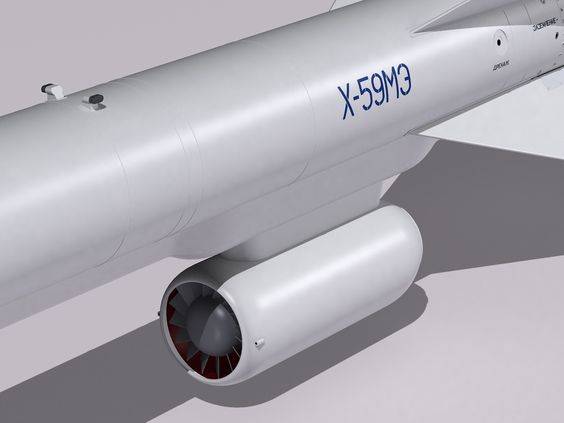

Specification
| Engine | 36МТ |
| Thrust at maximum rating, kgf | 450 |
| Maximum length, mm | 850 |
| Maximum diameter, mm | 330 |
| Weight, kg | <100 |
Source npo-saturn.ru
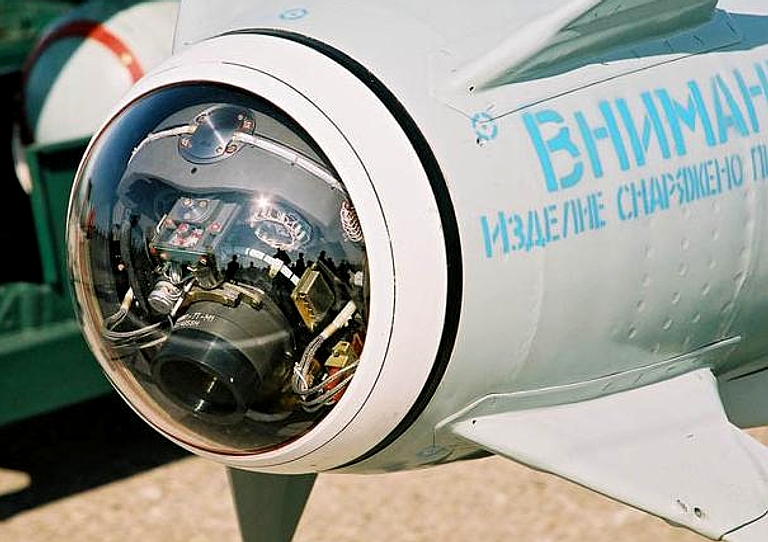
Target coordinates are fed into the missile before launch, and the initial flight phase is conducted under inertial guidance. At a distance of 10 km from the target the television guidance system is activated. An operator aboard the aircraft visually identifies the target and locks the missile onto it.
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 930 kg (2,050 lb) |
| Length | 570 cm (220 in) |
| Diameter | 38.0 cm (15.0 in) |
| Warhead | Cluster or shaped-charge fragmentatio |
| Warhead weight | 320 kg (705 lb) |
| Engine | Kh-59: two-stage rocket Kh-59ME: rocket then turbofan |
| Wingspan | 130 cm (51.2 in) |
| Operational range | Kh-59ME (export): 115 km (62 nmi) Kh-59ME: 200 km (110 nmi) Kh-59MK: 285 km (150 nmi) |
| Speed | Mach 0.72-0.88 |
| Guidance system | inertial guidance (then TV guidance), millimeter wave active radar seeker (Kh-59MK, Kh-59MK2 land attack version) |
| Launch platform | Kh-59ME: Su-30MK Kh-59: Su-24M, MiG-27, Su-17M3/22M4, HAL Tejas, Su-25 and Su-30 |
Source wikipedia.org
It is also armed with KAB-50OKR TV-guided and KAB-1500L laser-guided air bombs, supplied by the Region State Research and Production Enterprise of Moscow.
Kh-58 (Russian: Х-58; NATO:AS-11 ‘Kilter’)
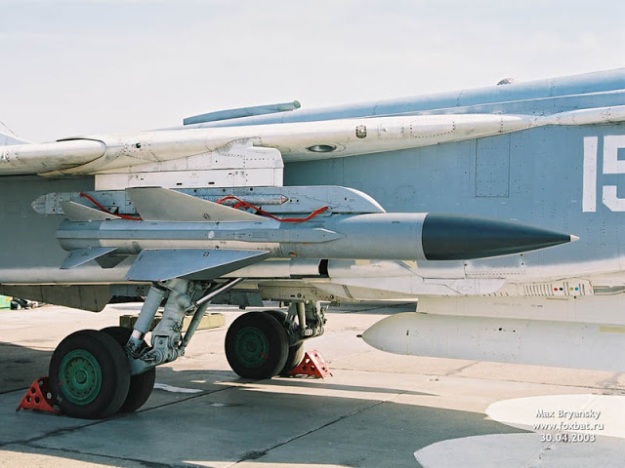

Kh-58 (Izdeliye 112) – original version for the Su-24M
The Kh-58E missile is designed to engage radars making part of land-based air defence systems, air defence early warning, target designation and control systems, and other emitting targets operating in A/A’, B/B’ and C frequency bands.
The Kh-58E missile can be employed in any weather conditions (rain, snow, fog) or season, without any restrictions on geographical latitude of the launch site.
The missile is guided by a passive radar homing head and an autonomous control system.
The Kh-58E missile can be employed in weapon systems of the Su-24MK, Su-22M4, Su-25TK, MiG-25BM type combat aircraft equipped with an appropriate target designation system and airborne ejection unit for missile’s launch.
Developer and manufacturer: “Raduga” State Machine-Building Design Bureau
Performance:
| Max range | |
| (depends on launch altitude at max speed), km | 46-200 |
| Launch altitudes, km | 0,2-20 |
| Launch speeds, Mach number | 0,47-2,35 |
| Min launch range, km | 8-60 |
| Missile launch weight, kg | 650 |
| Warhead weight, kg | 149 |
| Missile dimensions, m: | |
| length | 4,8 |
| body diameter | 0,38 |
| wing span | 1,17 |
Source ktrv.ru
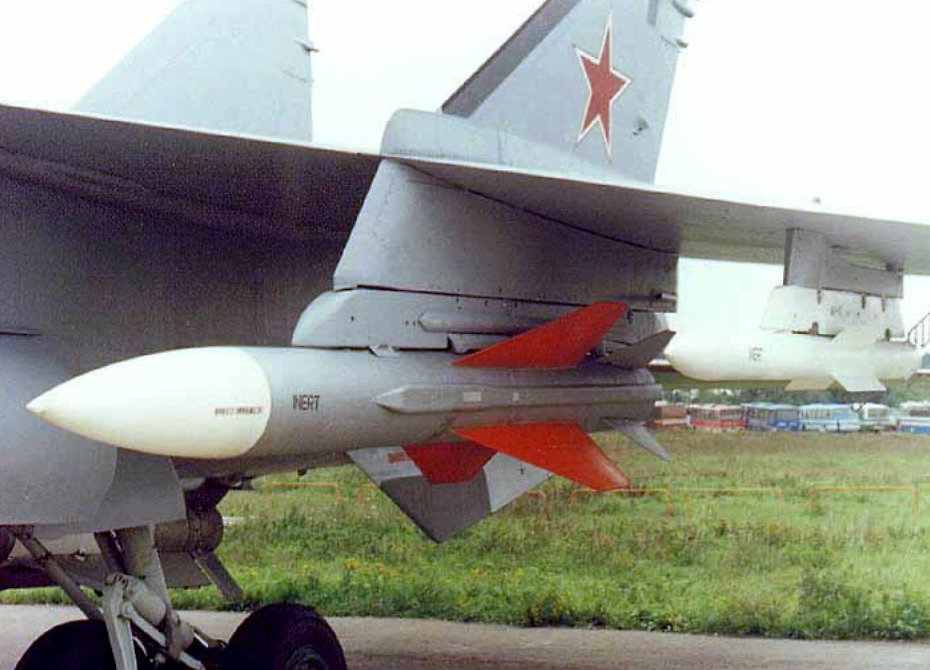
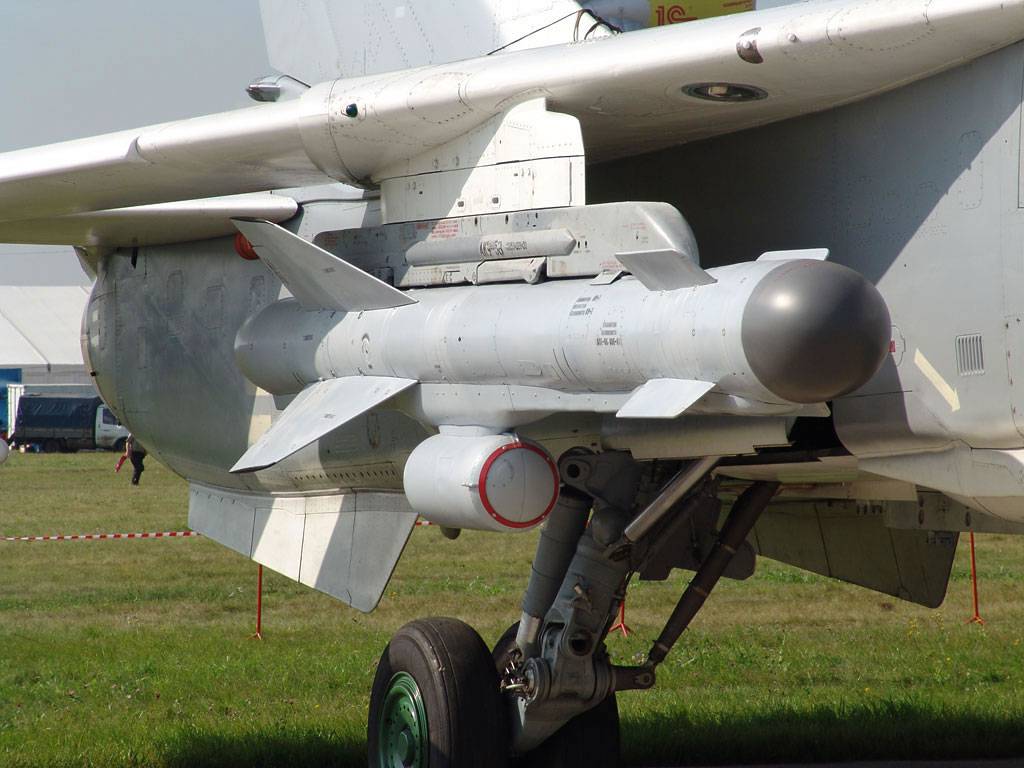
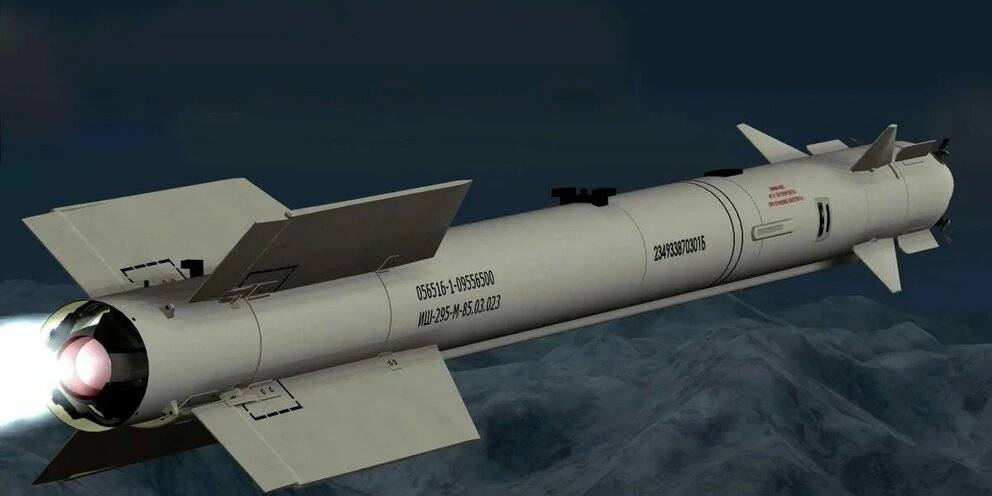
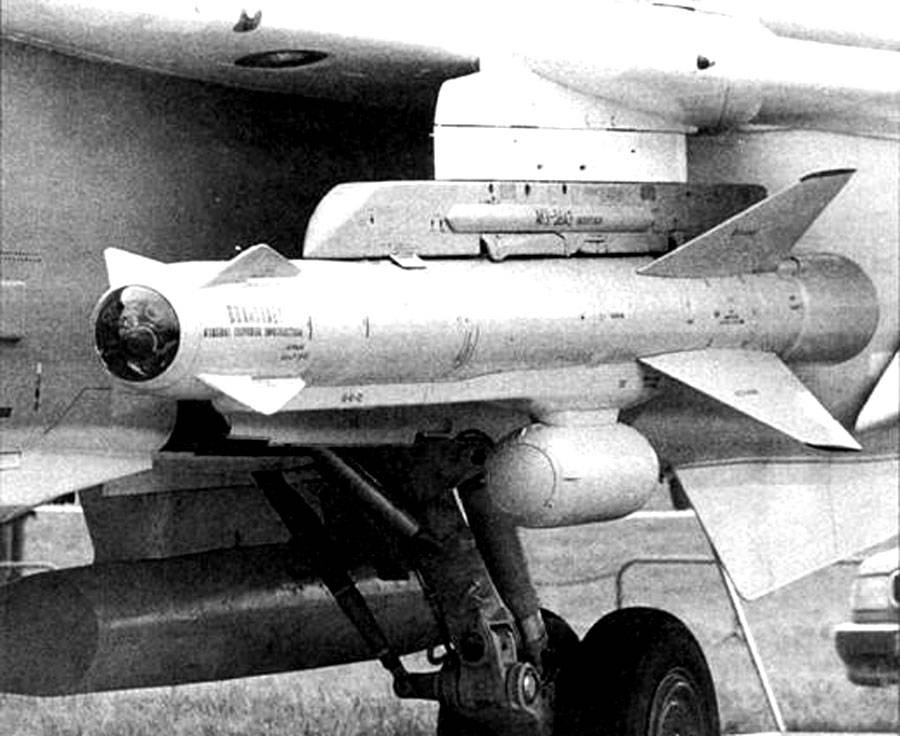
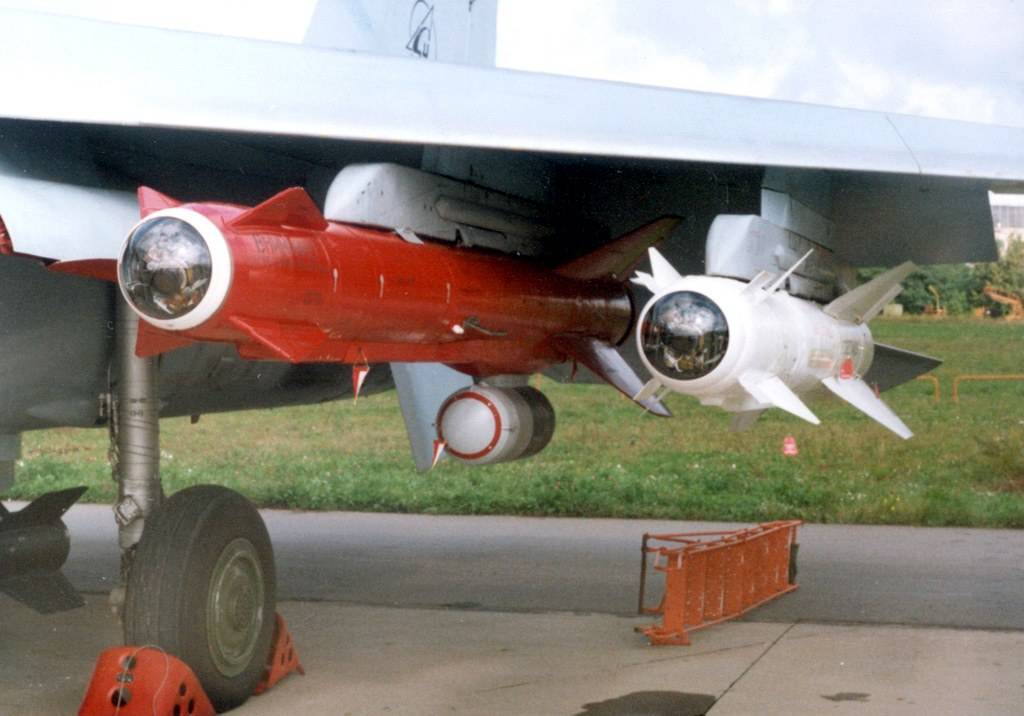
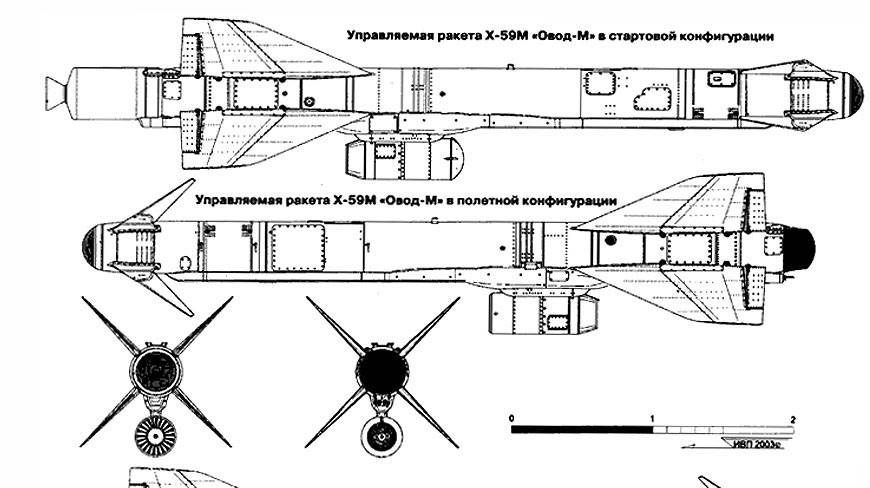















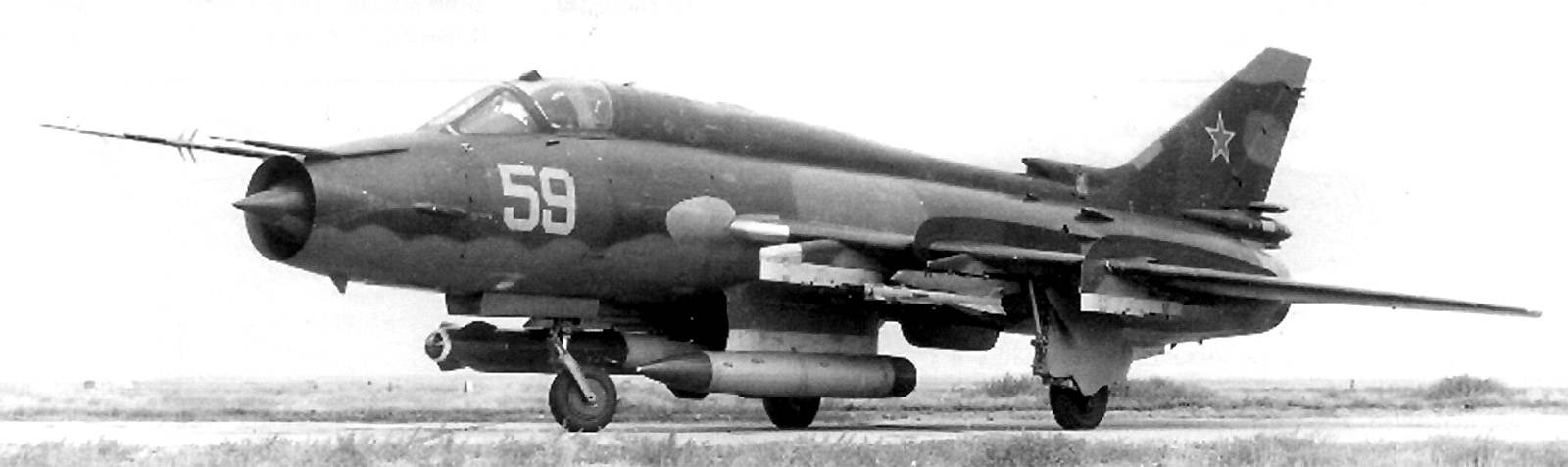
 Su-24 armed with Vympel R-60 and Kh-31 A/P missiles
Su-24 armed with Vympel R-60 and Kh-31 A/P missiles