Overview
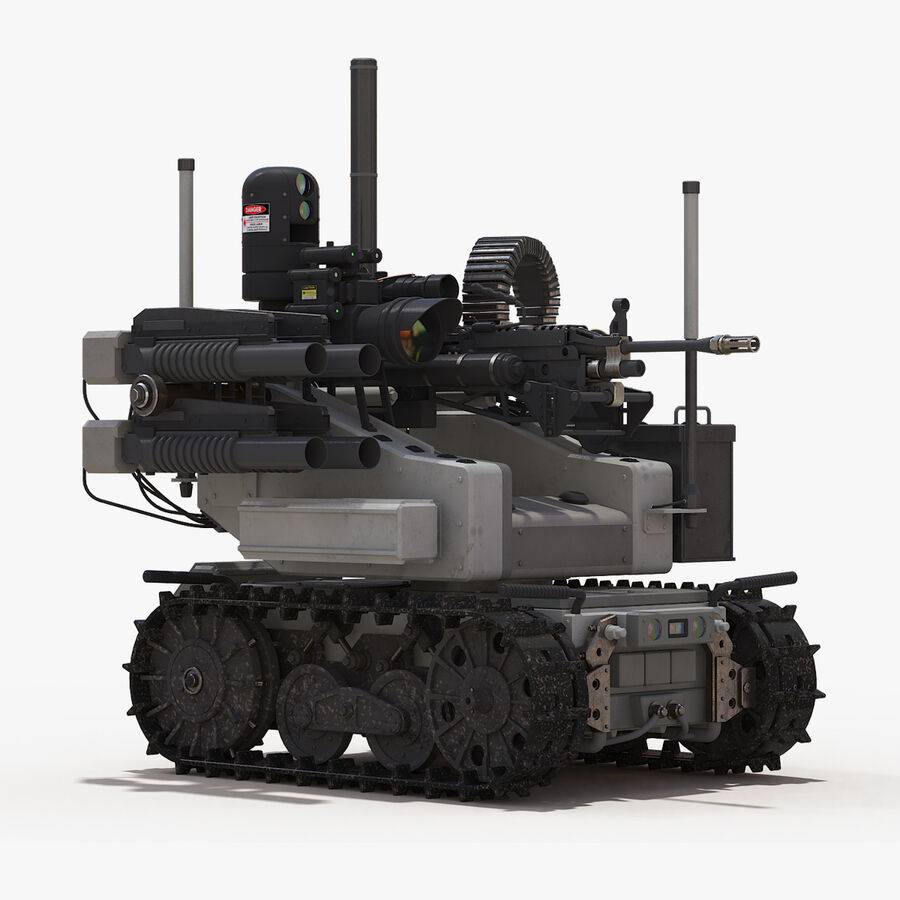
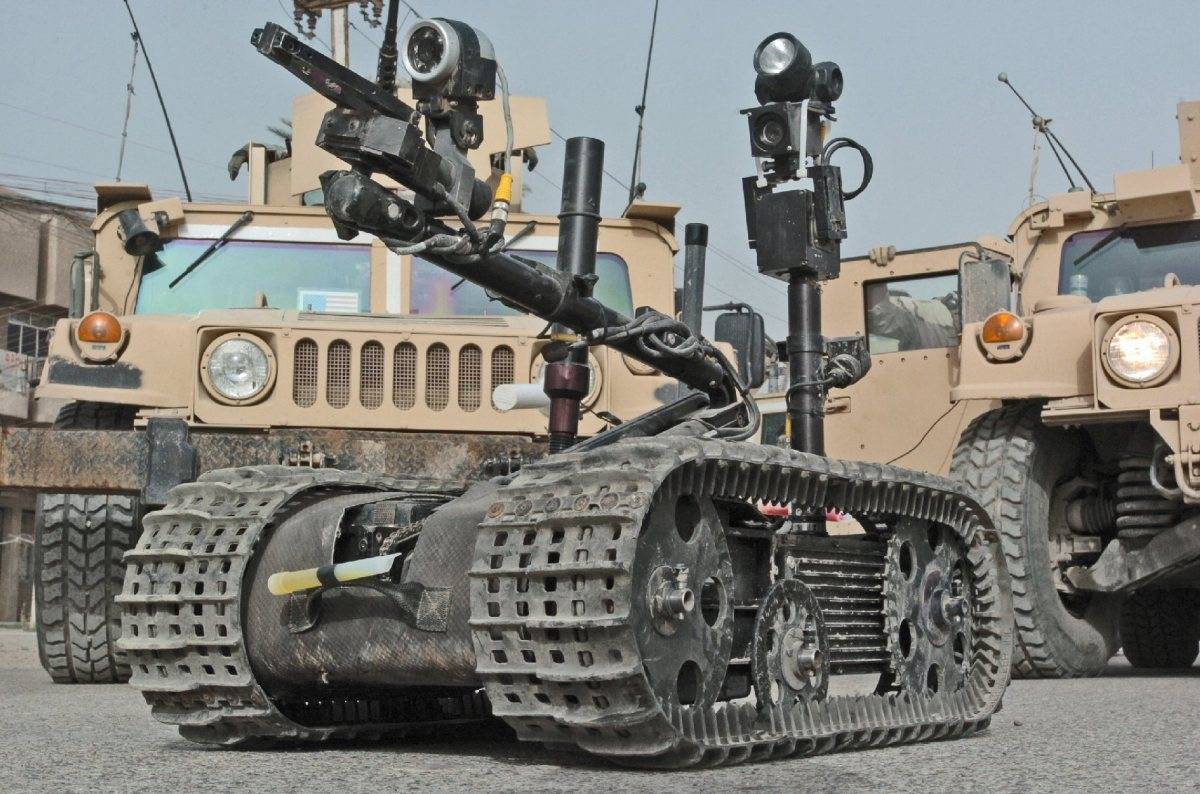
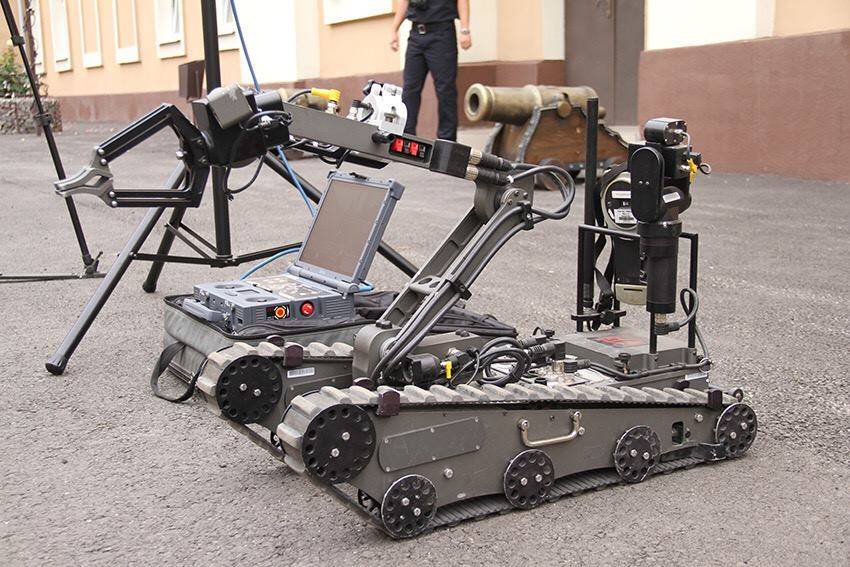
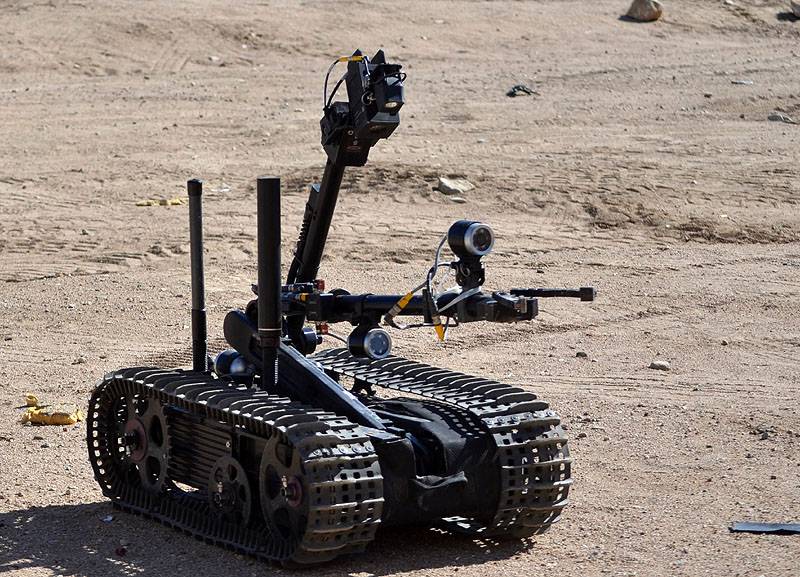
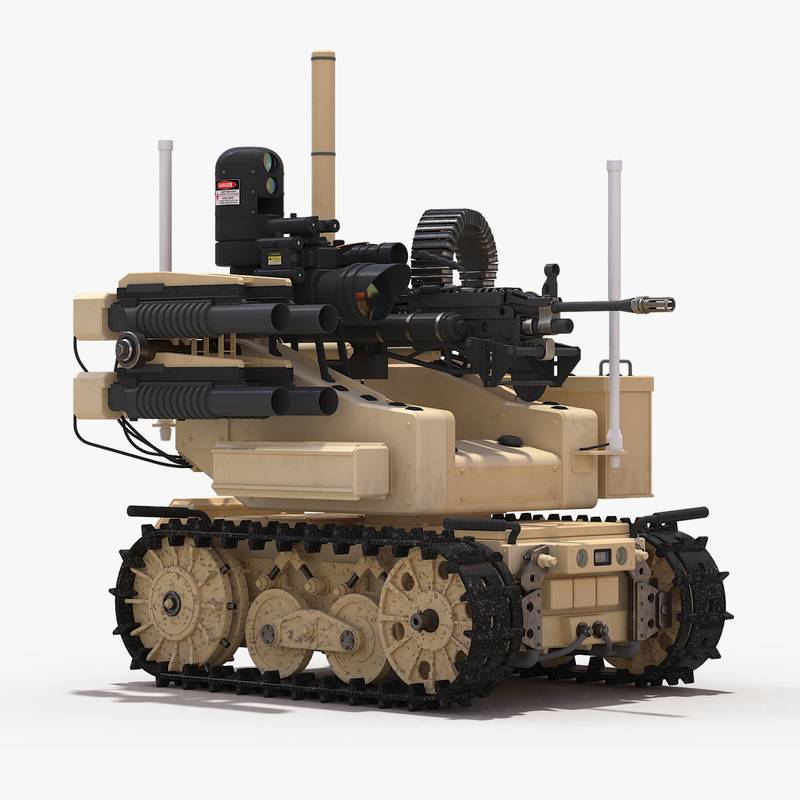
Foster-Miller claims the TALON is one of the fastest robots in production, one that can travel through sand, water, and snow, as well as climb stairs. The TALON transmits in color, black and white, infrared, and/or night vision to its operator who may be up to about 3,937ft (1,200m) away. It can run off lithium-ion batteries for a maximum of seven days on standby before needing to recharge. It has an 8.5-hour battery life at normal operating speeds, two standard lead batteries providing two hours each, and one optional lithium ion providing an additional 4.57 hours. It can withstand repeated decontamination, allowing it to work for extended periods of time in contaminated areas. It was used at Ground Zero after the September 11 attacks, working for 45 days under contaminated conditions without electronic failure. This led to the further development of the HAZMAT TALON.
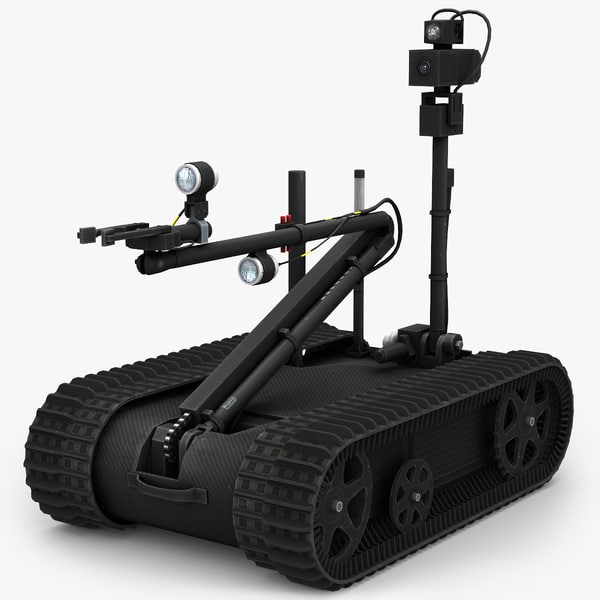
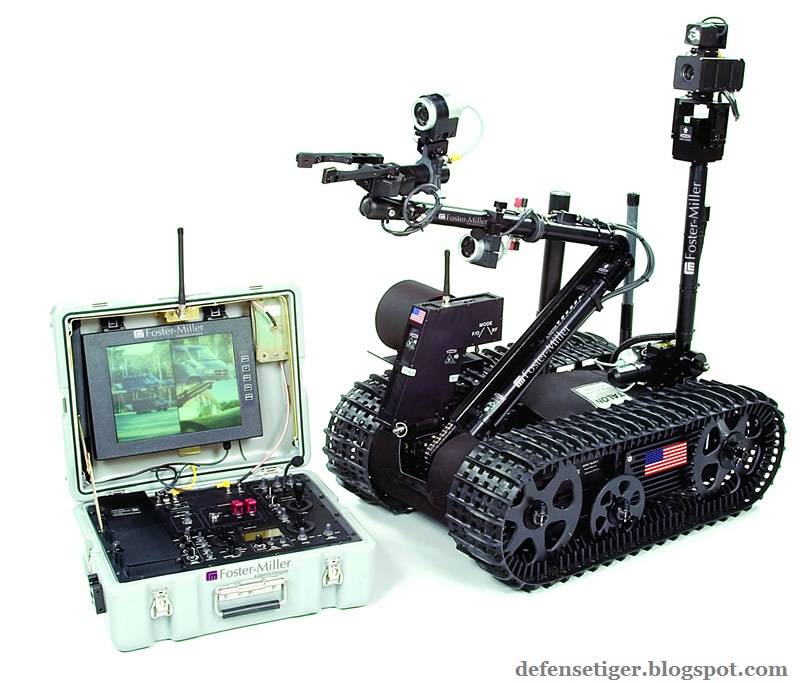
It weighs less than 100 pounds (45kg), or 60 pounds (27kg) for the reconnaissance version. Its cargo bay can accommodate a variety of sensor payloads. The robot is controlled through a two-way radio or fiber-optic link from a portable or wearable Operator Control Unit (OCU) that provides continuous data and video feedback for precise vehicle positioning.
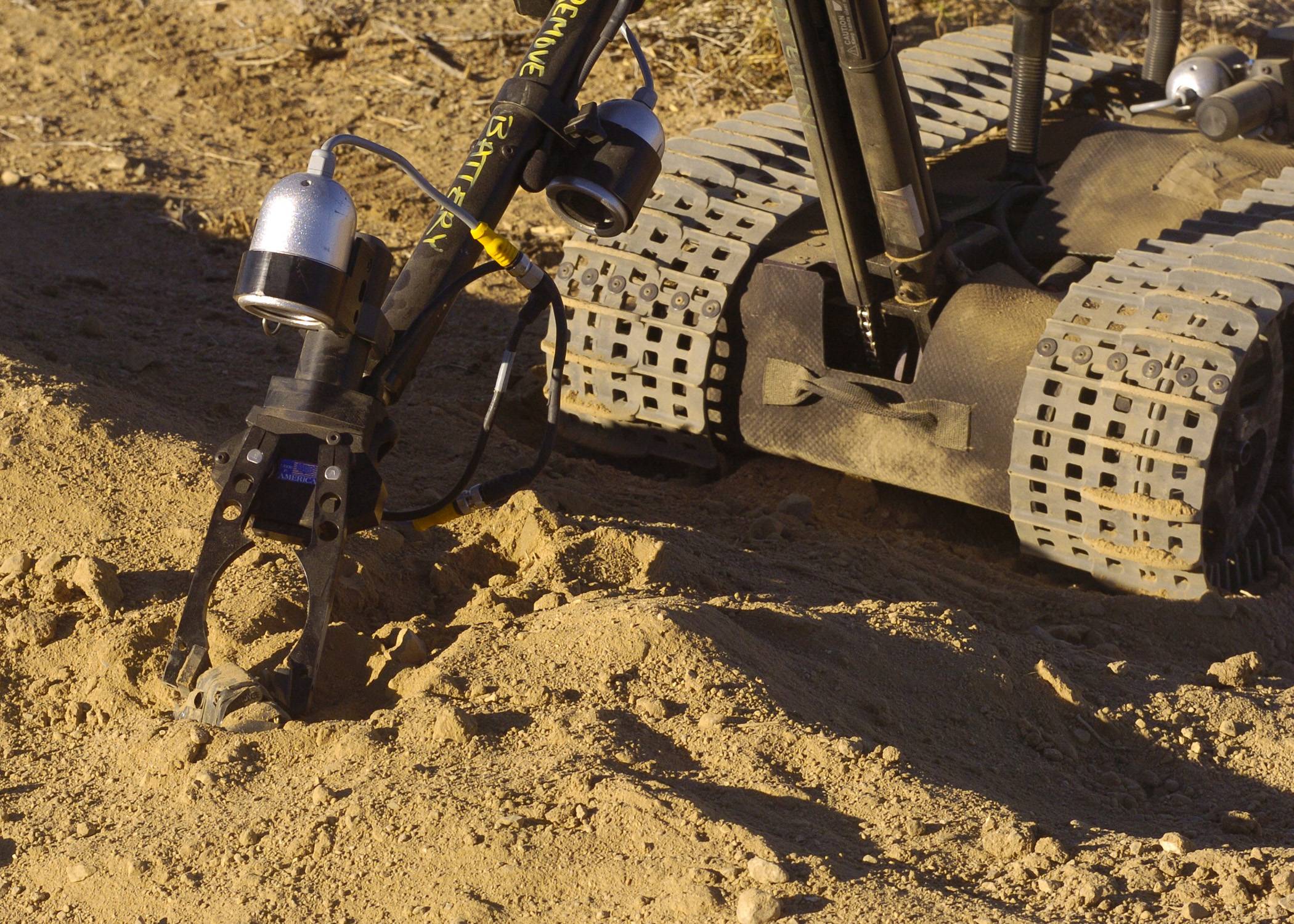
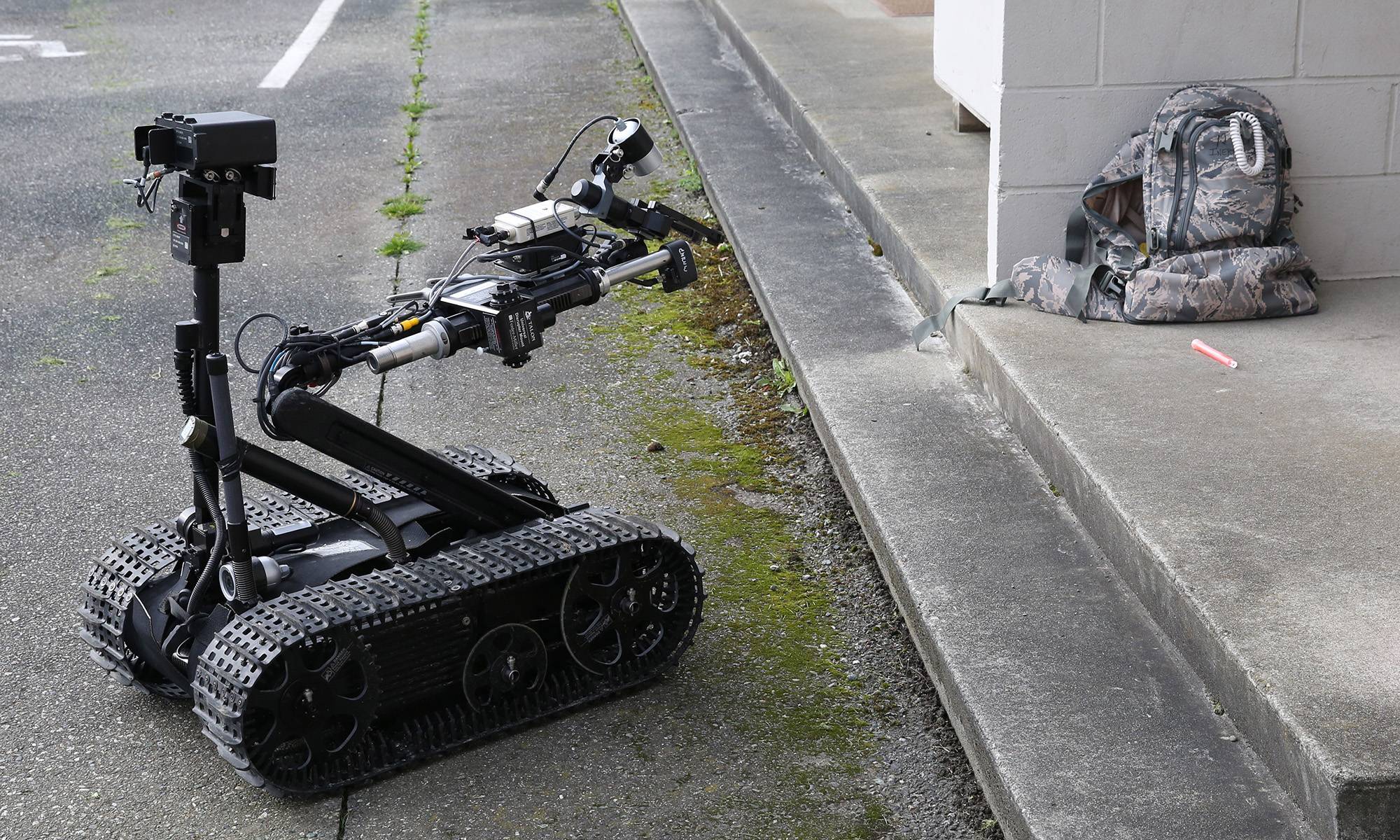
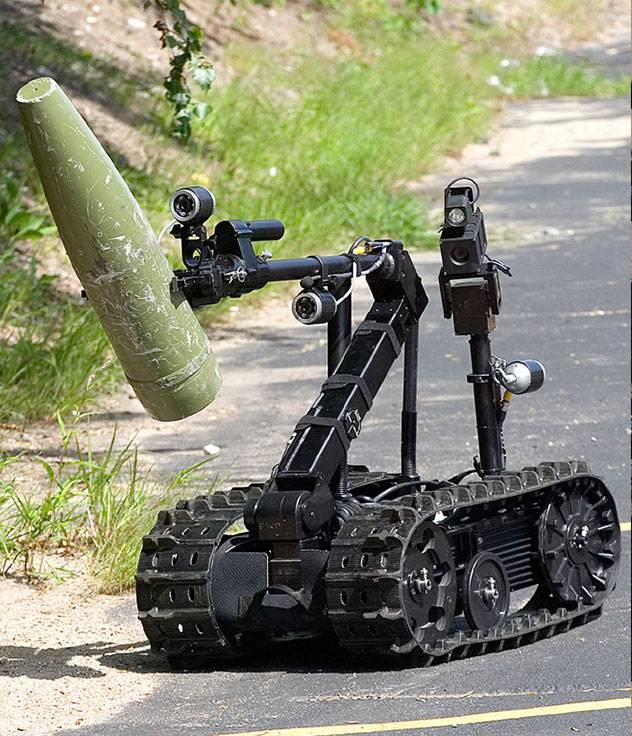
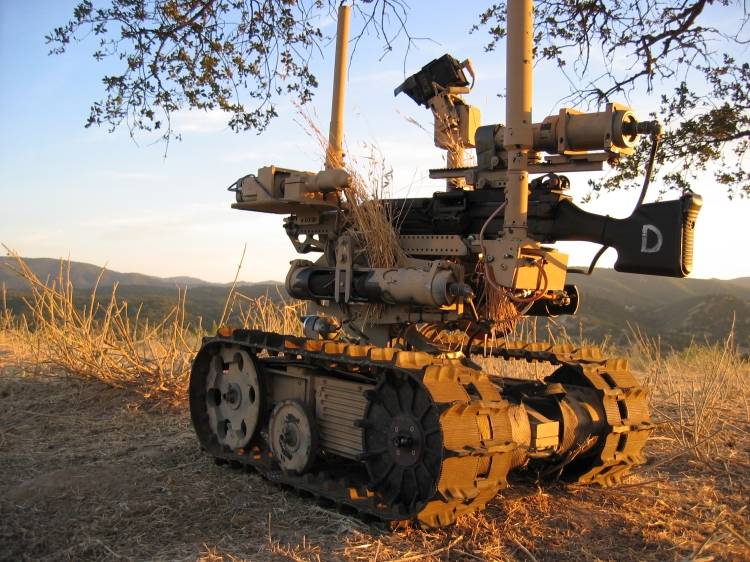
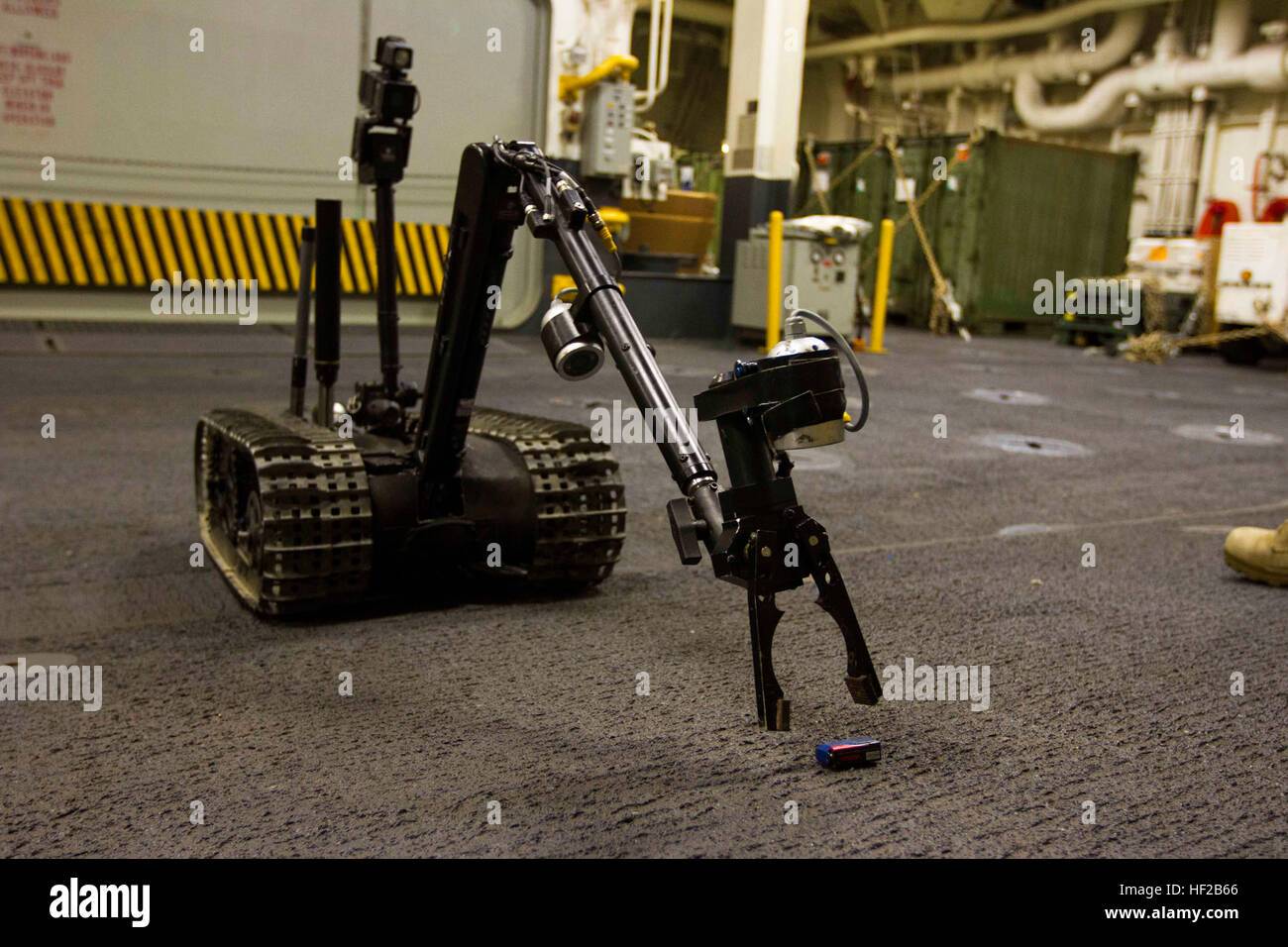
Regular (IED/EOD) TALON: Carries sensors and a robotic manipulator, which are used by the U.S. military for explosive ordnance disposal and disarming improvised explosive devices.
Special Operations TALON (SOTALON): Does not have the robotic arm manipulator but carries day/night color cameras and listening devices; lighter due to the absence of the arm, for reconnaissance missions.
SWORDS TALON: For small arms combat and guard roles. Evaluated in December 2003 in Kuwait prior to deployment in Iraq.
HAZMAT TALON: Uses chemical, gas, temperature, and radiation sensors that are displayed in real-time to the user on a hand-held display unit. It is now being evaluated by the US Armament Research Development and Engineering Centre (ARDEC).
C-TALON is an unmanned robot designed to be used in both land and water environments. It is specifically designed for turbulent water environments, coastal waters, and limited access harbors. It has high-resolution imaging sonar, among other key features.
Australian Defence Force selects QinetiQ’s TALON robots
27 August 2009
Devrim Esenturk
There are now more than 2,800 TALON robots deployed around the world
QinetiQ Group PLC, a leading international provider of technology-based services and solutions, has secured a AUS$23 million contract from the Australian Department of Defence for TALON robots and replacement parts to support Australian Defence Forces deployed on operations.
Developed by QinetiQ North America in Waltham, Massachusetts, TALON robots can be configured for specific tasks including the disposal of Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs), reconnaissance, the identification of hazardous material, combat engineering support and assistance to police units engaged in SWAT (Special Weapons and Tactics) operations. 2,800 TALON robots are deployed around the world – more than any other military robot.
“The TALON robot is an excellent example of the world-leading technology that QinetiQ is able to deliver to our clients within Australia and the region,” said Mike Kalms, CEO of QinetiQ Australia. “We continue to work closely with our UK and US colleagues to ensure QinetiQ is able to offer an increasing portfolio of leading technology and service solutions to our Australian defence customers.”
QinetiQ also provides a repair and maintenance facility for TALON robots in Australia and the region through its partner company, Pacific Security and Environmental Solutions.
Deployment
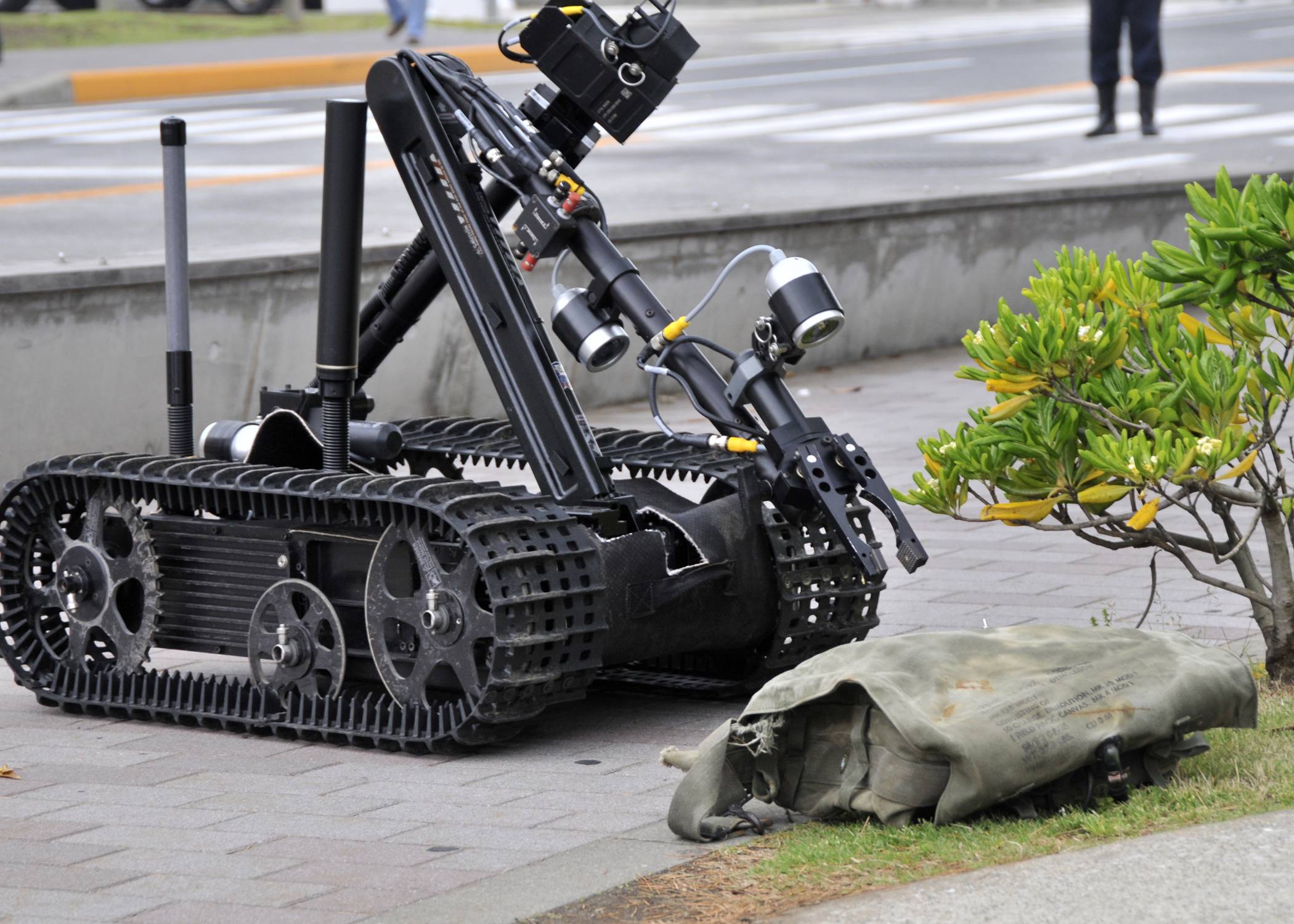
The Talon has been deployed in military service since 2000 – for example, in Bosnia for the movement of munitions and EOD (explosive ordnance disposal) to dispose of grenades. It was also used at Ground Zero after the September 11th attacks in search and recovery. It is the only robot used in this effort that did not require any major repair.[unreliable source?] Foster-Miller claims the Talon was used for a classified mission by US Special Forces in the war against the Taliban in Afghanistan, as well as in an EOD role. In Iraq, its standard role has been performing EOD and IED destruction missions. Its combat SWORDS version is now being used there as a guard protecting front line buildings from attack. According to Foster-Miller, the robot has performed around 20,000 EOD missions in the conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan.
As of late 2014, the Army was refurbishing 353 Talon IV robots, with 296 going to Army engineers and 57 for the Army National Guard.
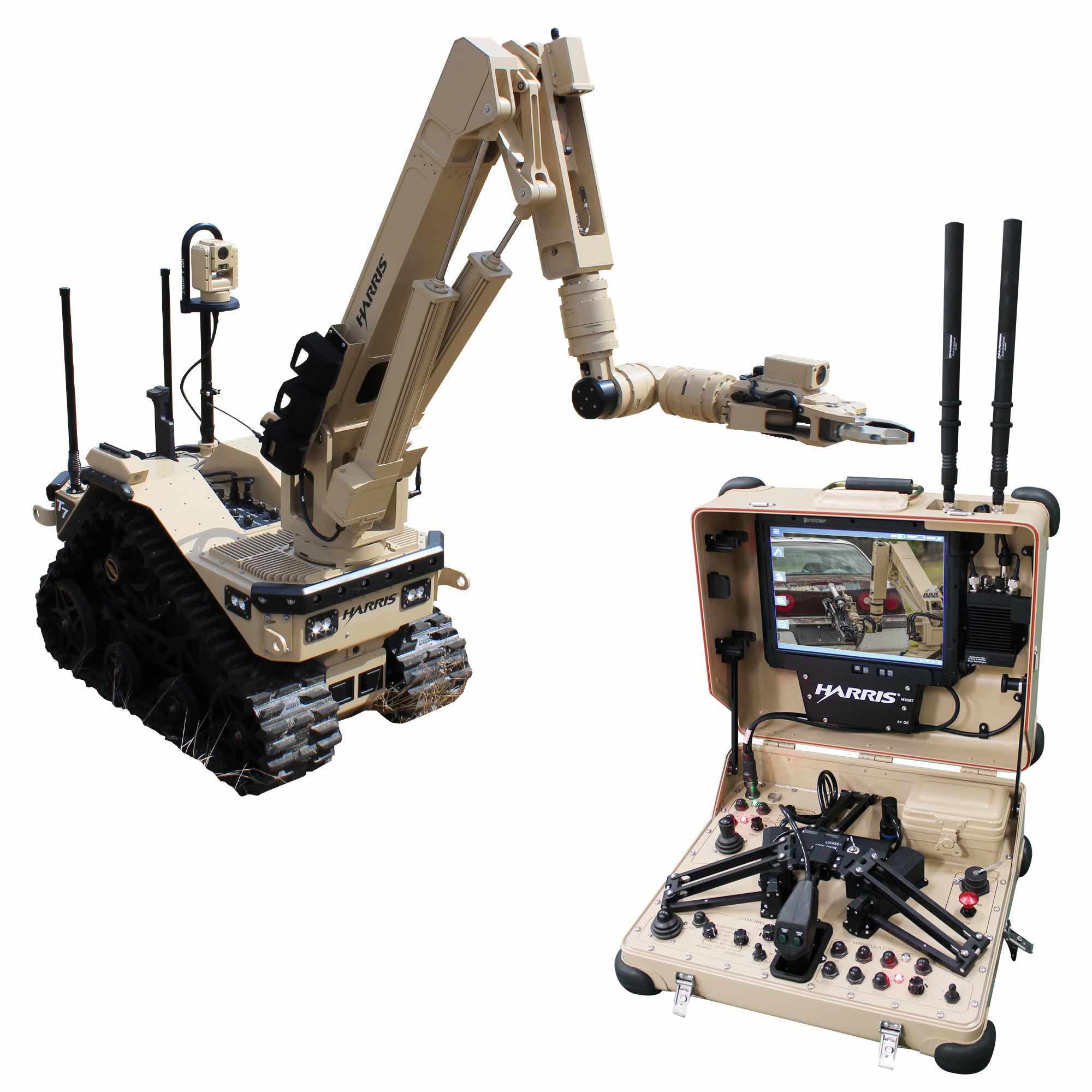
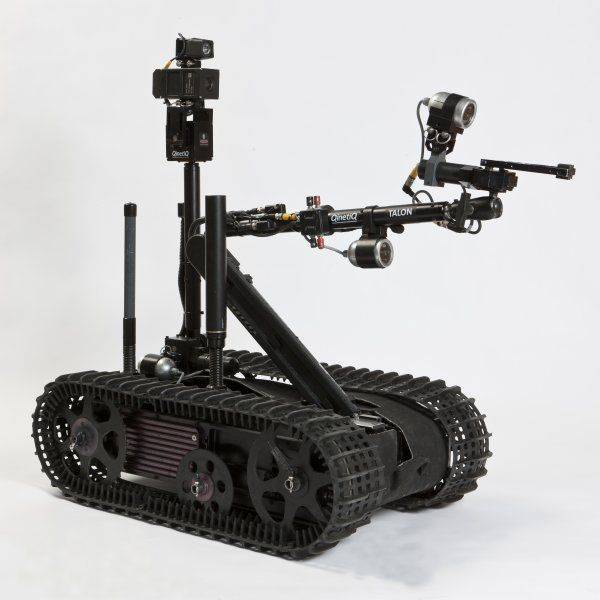
Talon Specifications
9 April 2010
Devrim Esenturk
TALON | ||

Talon New Arm Three degree of freedom shoulder
Lifting Strength
| Width | 57,2cm |
| Length | 86,4cm | |
| Height (Arm Stowed) | 42,7cm | |
| Height (Arm Extended) | 130cm | |
| Horizontal Reach | 130cm | |
| Below Grade Reach | 60cm | |
| Ground Clearance | 7cm | |
| Weight | 52 – 71kg | |
| Speed | 8,3km/h | |
| Payload Capacity | 45kg | |
| Drag Capacity with Grapper | 113kg | |
| Tow Capacity | 680kg | |
| Arm Lift Capacity | 4,5kg full extention 11kg max | |
| Gripper Capacity | 5,4kg/cm gripping strenght 15,2cm wide opening |
| Operation Control Unit (OCU) | Width Height Lenght Weight | 40,6cm 22,9cm 48,3cm 15kg | Batteries | Robot: Two Lead Acid, 300W, 36V, 2,8hr or One lithuim Ion, 750W, 36V, 4,5hr OCU: Nickel-Metal Hydride, 3,6A, 24V, 2hr or Lithuim-Ion, 4hr |
Cameras:
| Environmental: The TALON robot and its OCU are water resistant and designed to operate in a heavy downpour without protection. Equipment operates in all climates, weather, temperatures and conditions including mountains, deserts, snow/ice, demolition rubble and heavy wet mud. | |||
Communication:
| ||||
Options:
Sensors:
| ||||
Configurations:
|
МЕЧИ [ править ]
Подразделения ТАЛОННЫХ МЕЧЕЙ Фостера-Миллера, оснащенные различным вооружением.
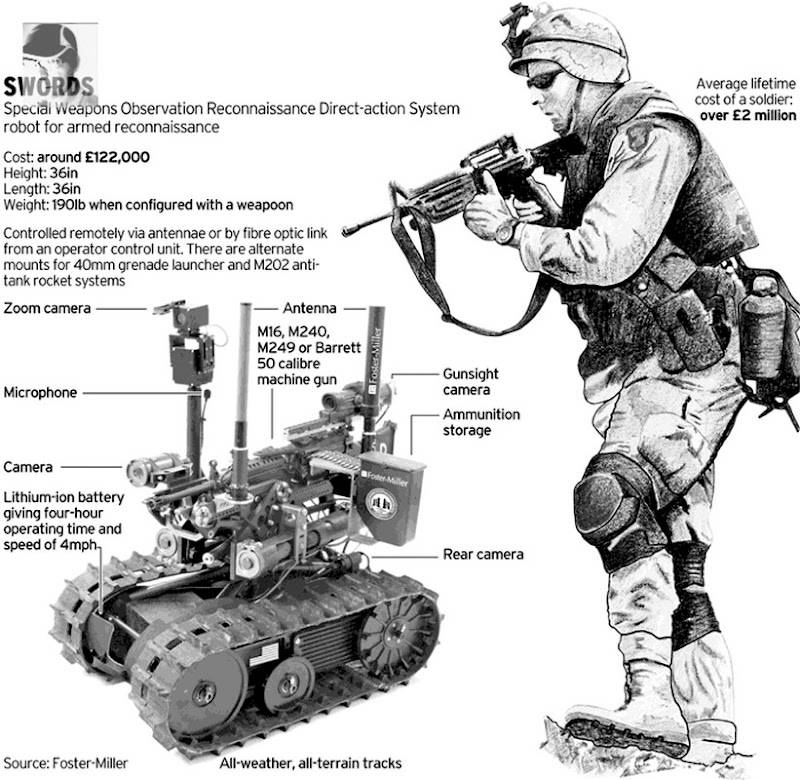
SWORDS или Система обнаружения разведки с помощью специального оружия – это версия с вооружением, разрабатываемая Фостером-Миллером для армии США. Робот состоит из системы вооружения, установленной на стандартном шасси TALON . Текущая цена одной единицы составляет 230 000 долларов США; тем не менее, Foster-Miller утверждает, что, когда он поступит в массовое производство, цена может упасть до 150–180000 долларов.
Есть множество различного оружия, которое можно разместить на МЕЧАХ; Винтовка M16 , 5,56-мм SAW M249 , 7,62-мм пулемет M240 , винтовка M82 Barrett .50 калибра , 40-мм шестиствольный гранатомет или счетное 66-мм зажигательное оружие M202A1 FLASH .
Отряды МЕЧЕЙ продемонстрировали способность стрелять точно. Он не является автономным, вместо этого солдат должен управлять им с помощью небольшой консоли, чтобы дистанционно управлять устройством и стрелять из его оружия. Фостер-Миллер в настоящее время работает над контроллером в стиле « Game Boy » с очками виртуальной реальности для будущих операторов.
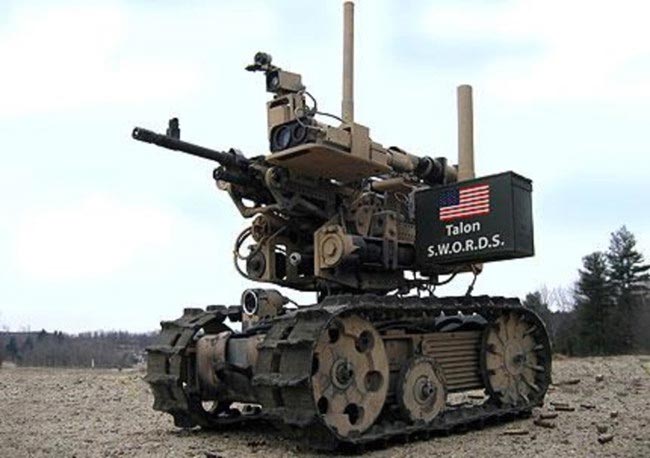
В 2007 году три подразделения SWORDS были переброшены в Ирак. Каждая часть вооружена пулеметом М249 . Это развертывание стало первым случаем, когда роботы несли в бой оружие; однако их оружие осталось неиспользованным, поскольку армия никогда не давала разрешения на его использование. Армия прекратила финансирование роботов SWORDS после развертывания первых трех роботов. Фостер-Миллер работает над преемником: усовершенствованной модульной вооруженной роботизированной системой (MAARS).
К августу 2013 года Смитсоновский институт приобрел для своей коллекции робота SWORDS. Один также выставлен в Национальном музее пехоты в Форт-Беннинге , штат Джорджия .
SWORDS
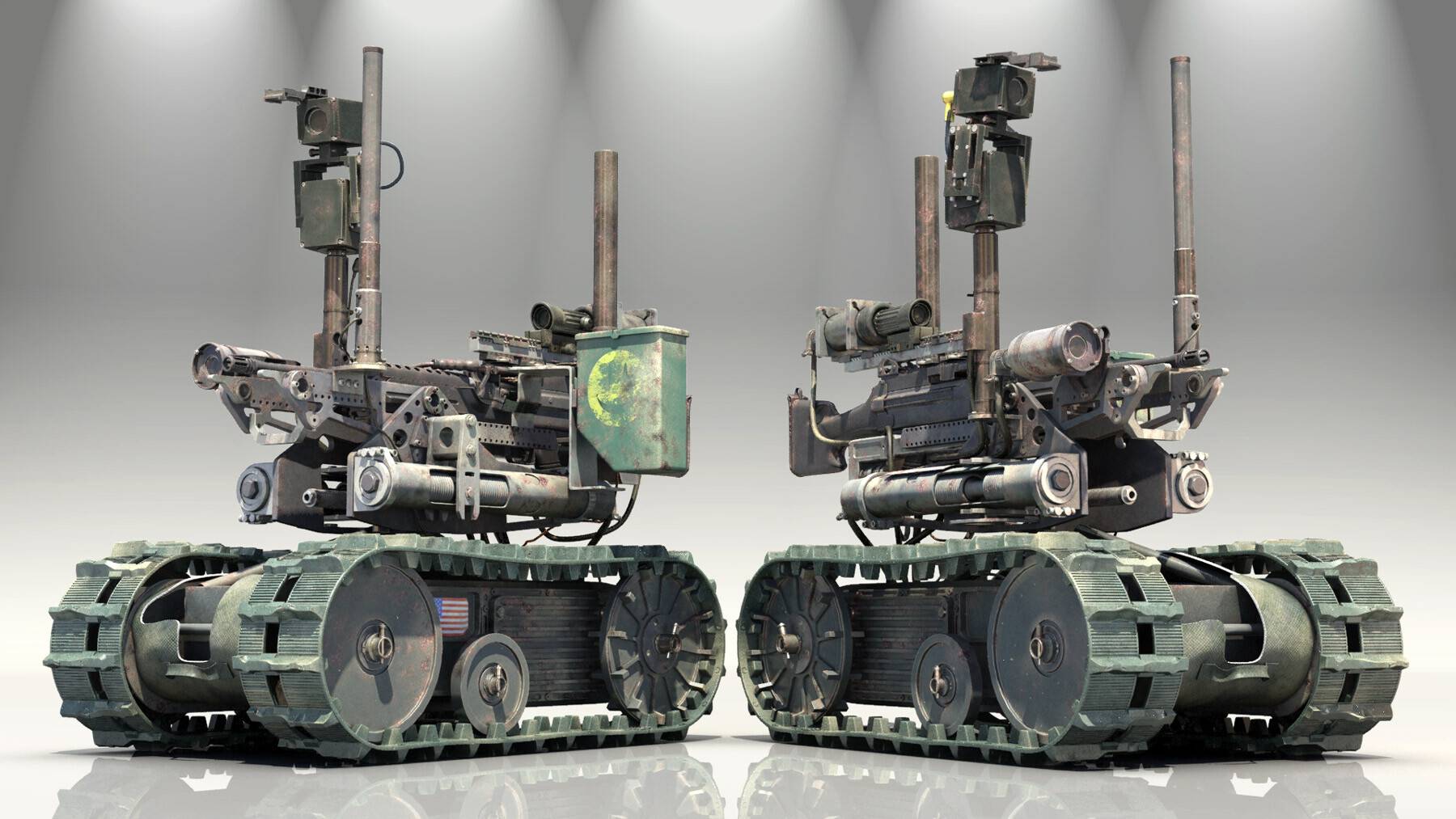
File:SWORDS.jpg
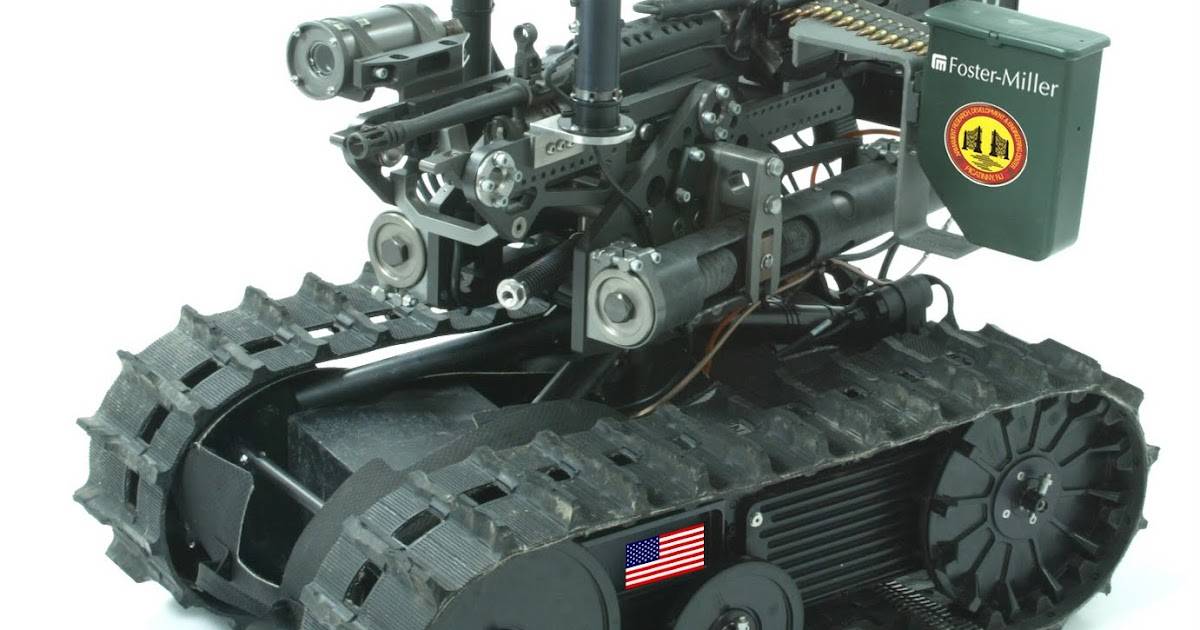
Foster-Miller TALON SWORDS units equipped with various weaponry.
SWORDS or the Special Weapons Observation Reconnaissance Detection System, is a weaponized version being developed by Foster-Miller for the US Army. The robot is composed of a weapons system mounted on the standard TALON chassis. The current price of one unit is $230,000; however, Foster-Miller claims that when it enters mass production the price may drop to between $150,000 and $180,000.
There are a variety of different weapons that can be placed on the SWORDS; M16 rifle, 5.56 mm SAW M249, 7.62 mm M240 machine gun, .50 cal M82 Barrett rifle, a six barreled 40 mm grenade launcher or quad 66 mm M202A1 FLASH incendiary weapon.
SWORDS units have demonstrated the ability to shoot precisely. It is not autonomous, but instead has to be controlled by a soldier using a small console to remotely direct the device and fire its weapons. Foster-Miller are currently at work on a “Game Boy” style controller with virtual-reality goggles for future operators.
In 2007, three SWORDS units were deployed to Iraq. Each unit is armed with a M249 machine gun. This deployment marks the first time that robots are carrying guns into battle; however, their weapons have remained unused as the Army has never given the go-ahead for using them. The Army stopped funding the SWORDS robots after deploying the initial three robots. Foster-Miller is working on a successor: the Modular Advanced Armed Robotic System (MAARS)
By August 2013, the Smithsonian Institution had acquired a SWORDS robot for its collection. One is also on display at the National Infantry Museum in Fort Benning, Georgia.
SWORDS
Foster-Miller TALON SWORDS units equipped with various weaponry.
SWORDS or the Special Weapons Observation Reconnaissance Detection System, is a weaponized version being developed by Foster-Miller for the US Army. The robot is composed of a weapons system mounted on the standard TALON chassis. The current price of one unit is $230,000; however, Foster-Miller claims that when it enters mass production the price may drop to between $150,000 and $180,000.
There are a variety of different weapons that can be placed on the SWORDS; M16 rifle, 5.56 mm SAW M249, 7.62 mm M240 machine gun, .50 cal M82 Barrett rifle, a six barreled 40 mm grenade launcher or quad 66 mm M202A1 FLASH incendiary weapon.
SWORDS units have demonstrated the ability to shoot precisely. It is not autonomous, but instead has to be controlled by a soldier using a small console to remotely direct the device and fire its weapons. Foster-Miller are currently at work on a “Game Boy” style controller with virtual-reality goggles for future operators.
In 2007, three SWORDS units were deployed to Iraq. Each unit is armed with a M249 machine gun. This deployment marks the first time that robots are carrying guns into battle; however, their weapons have remained unused as the Army has never given the go-ahead for using them. The Army stopped funding the SWORDS robots after deploying the initial three robots. Foster-Miller is working on a successor: the Modular Advanced Armed Robotic System (MAARS)
Deployment
The Talon has been deployed in military service since 2000 – for example, in Bosnia for the movement of munitions and EOD (explosive ordnance disposal) to get rid of grenades. It was also used in Ground Zero after the September 11th attacks in search and recovery. It is the only robot used in this effort that did not require any major repair. Foster-Miller claims the Talon was used for a classified mission by US Special Forces in the war against the Taliban in Afghanistan as well as in an EOD role. In Iraq its standard role has been performing EOD and IED destruction missions. Its combat SWORDS version is now being used there in a guard role protecting front line buildings from attack. According to Foster-Miller, the robot has performed around 20,000 EOD missions in the conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan.
Overview[]
Foster-Miller claims the TALON is one of the fastest robots in production, one that can travel through sand, water, and snow, as well as climb stairs. The TALON transmits in color, black and white, infrared, and/or night vision to its operator who may be up to about 3,937 ft (1,200 m) away. It can run off lithium-ion batteries for a maximum of seven days on standby before needing to recharge. It has an 8.5-hour battery life at normal operating speeds, two standard lead batteries providing two hours each, and one optional lithium ion providing an additional 4.57 hours. It can withstand repeated decontamination, allowing it to work for extended periods of time in contaminated areas. It was used at Ground Zero after the September 11 attacks, working for 45 days under contaminated conditions without electronic failure. This led to the further development of the HAZMAT TALON.
It weighs less than 100 pounds (45 kg), or 60 pounds (27 kg) for the reconnaissance version. Its cargo bay can accommodate a variety of sensor payloads. The robot is controlled through a two-way radio or fiber-optic link from a portable or wearable Operator Control Unit (OCU) that provides continuous data and video feedback for precise vehicle positioning.
Regular (IED/EOD) TALON: Carries sensors and a robotic manipulator, which are used by the U.S. military for explosive ordnance disposal and disarming improvised explosive devices.
Special Operations TALON (SOTALON): Does not have the robotic arm manipulator but carries day/night color cameras and listening devices; lighter due to the absence of the arm, for reconnaissance missions.
SWORDS TALON: For small arms combat and guard roles. Evaluated in December 2003 in Kuwait prior to deployment in Iraq.
HAZMAT TALON: Uses chemical, gas, temperature, and radiation sensors that are displayed in real-time to the user on a hand-held display unit. It is now being evaluated by the US Armament Research Development and Engineering Centre (ARDEC).
C-TALON is an unmanned robot designed to be used in both land and water environments. It is specifically designed for turbulent water environments, coastal waters, and limited access harbors. It has high-resolution imaging sonar, among other key features.
The robot costs approximately $6,000,000 in its standard form. Foster-Miller was subsequently bought out by QinetiQ, a United Kingdom military developer.
Sensors and communication
The TALON robot is mounted with up to seven cameras to provide soldiers with a comprehensive view of the ground for identification and detonation of suspicious objects from a safe distance.
The robot features fixed-focus infrared illuminated gripper-mounted camera, elbow and rear cameras, dimmable LED lights and a 26x optical-12x digital auto focus colour zoom camera (300:1). It can be optionally fitted with 200m camera (40:1), thermal colour or black and white cameras, MV-14 night vision, pan / tilt / mast and WARRVS / Fish Eye cameras.
The robot is equipped with one-way audio transmission with an option for two-way audio transmission. It uses USB and Ethernet communication ports and two RS 232 serial ports for payload interface. It can also be mounted with high-gain antenna with an extended LOS range of 1,200m.
Неприрожденные убийцы
В арсенале полиции Сан-Франциско имеется свыше десятка полнофункциональных роботов с дистанционным управлением, которые предназначены для осмотра территории, ведения наблюдения, обезвреживания боеприпасов, перемещения тяжелых предметов или разрушения стен. Управление машинами осуществляет оператор, который, по действующим правилам, обязан пройти предварительную подготовку по программе Федерального бюро расследований (ФБР) США.
Среди роботов, находящихся в распоряжении правоохранителей: модели F5A, 6A и RONS производства компании Remotec; Talon и Dragon Runner компании QinetiQ; IRobot FirstLook и ReconRobotics Recon Scout ThrowBot.
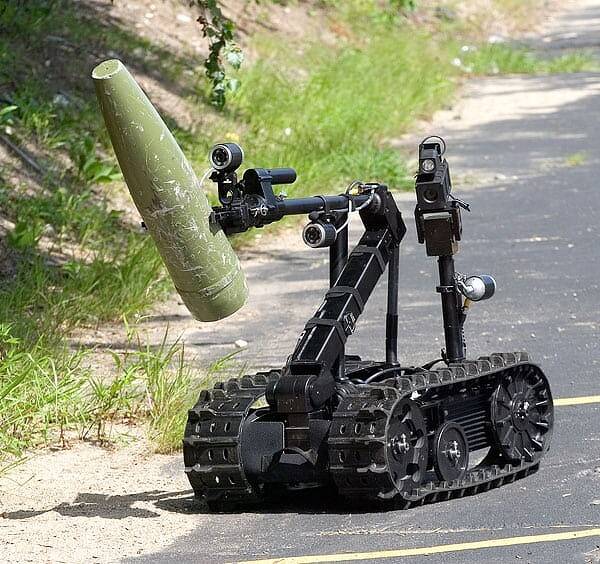 Робот-сапер Talon компании QiniQ
Робот-сапер Talon компании QiniQ
Ни одна из вышеупомянутых моделей в заводском исполнении не способна нести огнестрельное оружие. Remotec F5A, к примеру, представляет собой колесный агрегат, который может передвигаться по лестницам; имеет руку-манипулятор, способную поднимать объекты массой до 38,5 кг и таскать за собой другие тяжелые предметы.
Алексей Шовкун, «Информационные системы и сервисы»: Наша философия изначально строилась на использовании open source
ит в госсекторе

Однако в качестве орудия убийства подобные машины применяться все же могут.
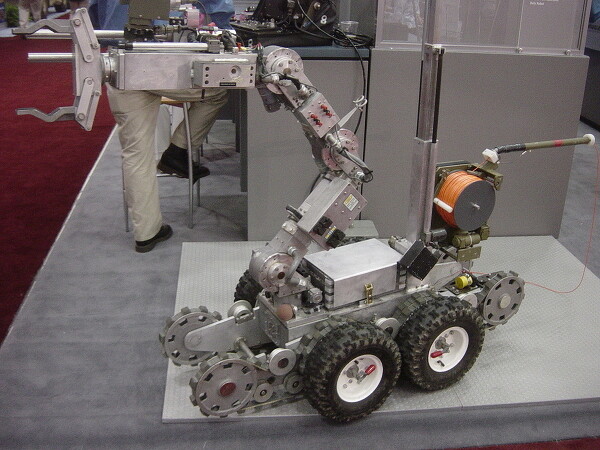 Робот-сапер Remotec Androd F6A
Робот-сапер Remotec Androd F6A
Так, в 2016 г. полиция Далласа (Техас) прикрепила к роботу-саперу Remotec Androx Mark V A-1 около 223 граммов пластичной взрывчатки C4 и направила его к стене, за которой скрывался снайпер, убивший двоих и ранивший еще нескольких сотрудников правопорядка. Когда машина оказалась у цели, оператор с безопасного расстояния активировал взрывное устройство, которое разрушило преграду и смертельно поразило преступника. Робот, рыночная цена которого на тот момент составляла около $151 тыс., при этом практически не пострадал. Это был первый случай применения робота для ликвидации преступника в США.
Кроме того, как отмечает Engadget, некоторые роботы, предназначенные для обезвреживания взрывчатки, допускают крепление специального приспособления для разрушения внутренней структуры взрывного устройства. Процедура предусматривает выстрел холостым патроном дробовика либо мощной струей воды в цель с близкого расстония. В теории ничто не мешает полиции заменить холостой патрон на боевой, тем самым превратив радиоуправляемого робота-сапера в механического убийцу.
Шолу
Фостер-Миллер TALON өндірістегі ең жылдам роботтардың бірі, ол құм, су және қар арқылы жүріп, баспалдақпен көтеріле алады деп мәлімдейді. TALON түрлі-түсті, ақ-қара, инфрақызыл, және / немесе түнгі көру 1000 м қашықтықта болуы мүмкін оның операторына. Ол іске қосылуы мүмкін литий-ионды аккумуляторлар қажет болғанға дейін күту режимінде ең көбі 7 күн зарядтау. Қалыпты жұмыс жылдамдығында батареяның қызмет ету мерзімі 8,5 сағатты құрайды, әрқайсысы 2 сағаттан тұратын 2 стандартты қорғасын батареясы және қосымша 4,57 сағатты құрайтын 1 литий ионы. Ол сонымен қатар ластанған жерлерде ұзақ уақыт жұмыс істеуге мүмкіндік беретін бірнеше рет залалсыздандыруға төтеп бере алады. Бұл қолданылған Жердегі нөл кейін 11 қыркүйек шабуылдары 45 күн бойы көптеген залалсыздандырулармен электронды ақаусыз жұмыс істейді. Бұл одан әрі дамуына әкелді ХАЗМАТ TALON.
Оның барлау нұсқасы үшін салмағы 100 фунттан (45 кг) немесе 60 фунттан (27 кг) аз. Оның жүк қоймасында сенсорлардың әртүрлі жүктемелері бар. Робот a арқылы басқарылады екі жақты радио немесе а талшықты-оптикалық байланыс портативті немесе тозуға болатын операторды басқару блогынан (OCU) көлік құралының нақты орналасуы үшін үздіксіз деректер мен бейнебақылауды қамтамасыз етеді.
Тұрақты (IED / EOD) TALON: сенсорлар мен роботтық манипуляторды алып жүреді, оны АҚШ әскери күші қолданады. жарылғыш заттарды жою және қарусыздану қолдан жасалған жарылғыш құрылғылар.
Арнайы операциялар TALON (SOTALON): роботты қол манипуляторы жоқ, бірақ күндіз / түнде түс береді камералар және тыңдау құрылғылары; қолдың болмауына байланысты жеңілірек, барлау миссиялары үшін.
ҚЫЛЫШТАР ТАЛОНЫ: Қару-жарақ пен жауынгерлік рөлдерге арналған. 2003 жылы желтоқсанда сыналған Кувейт орналастыруға дейін Ирак.
HAZMAT TALON: қолданады химиялық, газ, температура, және радиация нақты уақыт режимінде қолданушыға көрсетілетін дисплей блогында көрсетілетін датчиктер. Қазір оны АҚШ-тың қару-жарақты зерттеу және дамыту орталығы сынақтан өткізіп жатыр ARDEC.
Робот стандартты түрде шамамен $ 6,000,000 тұрады. Фостер-Миллерді кейіннен сатып алған QinetiQ, а Біріккен Корольдігі әскери әзірлеуші.
SWORDS
Foster-Miller TALON SWORDS units equipped with various weaponry
SWORDS, or the Special Weapons Observation Reconnaissance Detection System, is a weaponized version being developed by Foster-Miller for the US Army. The robot is composed of a weapons system mounted on the standard TALON chassis. The current price of one unit is $230,000; however, Foster-Miller claims that when it enters mass production the price may drop to between $150,000 and $180,000.
There are a variety of different weapons which can be placed on the SWORDS: M16 rifle, 5.56 mm SAW M249, 7.62 mm M240 machine gun, .50 cal M82 Barrett rifle, six barreled 40 mm grenade launcher or quad 66 mm M202A1 FLASH incendiary weapon.
SWORDS units have demonstrated the ability to shoot precisely. It is not autonomous, but instead has to be controlled by a soldier using a small console to remotely direct the device and fire its weapons. Foster-Miller are currently at work on a “Game Boy” style controller with virtual-reality headsets for future operators.
In 2007, three SWORDS units were deployed to Iraq. Each unit is armed with a M249 machine gun. This deployment marked the first instance of robots carrying guns into battle; however, their weapons have remained unused as the Army has never given authorization for using them. The Army stopped funding the SWORDS robots after deploying the initial three robots. Foster-Miller is working on a successor: the Modular Advanced Armed Robotic System (MAARS).
By August 2013, the Smithsonian Institution had acquired a SWORDS robot for its collection. One is also on display at the National Infantry Museum in Fort Benning, Georgia.
Overview[edit]
Foster-Miller claims the TALON is one of the fastest robots in production, one that can travel through sand, water, and snow, as well as climb stairs. The TALON transmits in color, black and white, infrared, and/or night vision to its operator who may be up to about 3,937 ft (1,200 m) away. It can run off lithium-ion batteries for a maximum of seven days on standby before needing to recharge. It has an 8.5-hour battery life at normal operating speeds, two standard lead batteries providing two hours each, and one optional lithium ion providing an additional 4.57 hours. It can withstand repeated decontamination, allowing it to work for extended periods of time in contaminated areas. It was used at Ground Zero after the September 11 attacks, working for 45 days under contaminated conditions without electronic failure. This led to the further development of the HAZMAT TALON.
It weighs less than 100 pounds (45 kg), or 60 pounds (27 kg) for the reconnaissance version. Its cargo bay can accommodate a variety of sensor payloads. The robot is controlled through a two-way radio or fiber-optic link from a portable or wearable Operator Control Unit (OCU) that provides continuous data and video feedback for precise vehicle positioning.
Regular (IED/EOD) TALON: Carries sensors and a robotic manipulator, which are used by the U.S. military for explosive ordnance disposal and disarming improvised explosive devices.
Special Operations TALON (SOTALON): Does not have the robotic arm manipulator but carries day/night color cameras and listening devices; lighter due to the absence of the arm, for reconnaissance missions.
SWORDS TALON: For small arms combat and guard roles. Evaluated in December 2003 in Kuwait prior to deployment in Iraq.
HAZMAT TALON: Uses chemical, gas, temperature, and radiation sensors that are displayed in real-time to the user on a hand-held display unit. It is now being evaluated by the US Armament Research Development and Engineering Centre (ARDEC).
C-TALON is an unmanned robot designed to be used in both land and water environments. It is specifically designed for turbulent water environments, coastal waters, and limited access harbors. It has high-resolution imaging sonar, among other key features.
The robot costs approximately $6,000,000 in its standard form. Foster-Miller was subsequently bought out by QinetiQ, a United Kingdom military developer.
MQ-1 Predator
MQ-1 Predator (ˈpredətə ˈв переводе англ. Хищник ) — разведывательный и ударный беспилотный летательный аппарат производства General Atomics (США). Первый полёт состоялся в 1994 году. Стоит на вооружении ВВС США. Активно применяется в данный момент на территории Ирака и Афганистана.
ТТХ:
• Размах крыла, м: 14,84 • Длина самолета, м: 8,23 • Высота, м: 2,21 • Масса, кг пустого: 512 максимальная взлетная: 1020 • Тип двигателя: 1 x ПД Rotax 914 UL • Мощность, л.с.: 105 • Максимальная скорость, км/ч: 217 • Крейсерская скорость, км/ч: 110—130 • Дальность полета, км: 740 • Продолжительность полета, ч нормальная более: 20 максимальная: 40 • Практический потолок, м: 7920
БПЛА Predator B был создан на базе успешного многоцелевого БПЛА RQ/MQ-1 Predator фирмы General Atomic Aeronautical Systems Inc. (GA-ASI). Работы надо Predator B были начаты в частном порядке в 1998 г., но частично финансировались NASA. Первый полет прототипа состоялся в феврале 2001 г. Было выпущено 3 прототипа YMQ-9A: • Predator B-001- первая модернизация БПЛА MQ-1 Predator. На него установлен турбовинтовой двигатель (712 кВт). Визуальное отличие от MQ-1 представляют крылья, они увеличены с 14,8 м. до 20 м. B-001 может нести 340 кг. полезной нагрузки на высоте 15,2 км., со скоростью 390 км/ч. Время полета до 30 часов. • Predator B-002 — следующая модернизация БЛА. Грузоподъемность 215 кг., верхний потолок высоты 18,3 км., время полета 12 часов. • Predator B-003 или «Альтаир» — снова увеличен размах крыльев, до 25,6 м. Следовательно, увеличенная грузоподъемность БЛА до 1360 килограммов, а максимальная высота полета 15,8 км. Время полета увеличено до 36 часов! БПЛА Predator B представляет собой увеличенный вариант RQ/MQ-1 Predator. Основным отличием является «более традиционное» V-образное хвостовое оперение, имеющее положительную V-образность. Фирма GA-ASI испытывала прототипы Predator B с двумя разными двигателями. Первый — ТВД фирмы Honeywell TPE-331-10T, а второй — ТРДД фирмы Williams FJ44-2A. Оборудование Predator B в основном идентично оборудованию RQ/MQ-1, и состоит из широкодиапазонной инфракрасной оптико-электронной прицельной системы Raytheon AN/ASS-52(V) и РЛС с синтезируемой апертурой AN/APY-8 Lynx фирмы General Atomics. Predator B так же может использоваться как многоцелевой боевой комплекс, вооруженный ПТУР AGM-114C/K Hellfire и другим управляемым оружием. Аппаратура управления БПЛА совместима с наземным оборудованием MQ-1B. После успешных экспериментов с вооруженным RQ-1 возникла идея отработать применение оружия и с борта Predator B. В феврале 2003 г. БПЛА Predator B в варианте с ТВД, получил обозначение MQ-9A Reaper. И в конце года ВВС США закупили два опытных БПЛА YMQ-9A. Были проведены войсковые испытания этих машин. YMQ-9A продемонстрировали высокие, весьма превосходящие характеристики своего «родителя». БПЛА показали находится в воздухе до 24 часов на высоте 13700 м, а по заявлению фирмы GA-ASI максимальная продолжительность полета составляет 30 часов. Новейший беспилотный самолет MQ-9 Reaper по классификации ВВС США относится к разряду «охотников-убийц» — самолетов, способных выслеживать цель и уничтожать ее. MQ-9 Reaper способен нести до 14 ракет Hellfire класса воздух-земля, в то время как широко используемый сейчас беспилотный самолет Predator вооружен только двумя такими ракетами. В случае необходимости вместо ракет MQ-9 Reaper может нести 4 AGM-114 «Хеллфайр» и две бомбы лазерного наведения — GBU-12 Paveway II по 250 килограмм каждая. MQ-9 Reaper с полной нагрузкой может непрерывно находиться в воздухе в течение 14 часов и имеет максимальную скорость 480 километров в час, тогда как максимальная скорость самолета Predator не превышает 215 километров в час. 18 мая 2006 года Федеральное управление гражданской авиации выдало сертификат соответствия, что позволяет MQ-1 и MQ-9 летать в воздушном пространстве США предназначенном для гражданских перевозок. Для ВМС США создается беспилотный аппарат на основе Reaper, названный «Mariner». Этот аппарат будет иметь складные крылья, увеличенный запас топлива, который позволит беспилотнику находиться в полете 49 часов. В августе 2008 года ВВС США завершили перевооружение беспилотными летательными аппаратами MQ-9 Reaper первой боевой авиачасти — 174-го истребительного авиакрыла Национальной гвардии. Перевооружение происходило в течение трёх лет. Ударные БПЛА показали высокую эффективность в Афганистане и Ираке. Основные преимущества перед заменёнными F-16: меньшая стоимость закупки и эксплуатации, большая продолжительность полёта, безопасность операторов и возможность их посменной работы при продолжительных полетах.























![Р-2 (ракета)содержание а также описание [ править ]](https://gunsfriend.ru/wp-content/uploads/6/4/3/643a0c0989d3a13945865f30e87543d2.jpeg)